The Beta coefficient is a measure of the risk and volatility of a stock or investment portfolio compared to the overall market. Understanding the Beta value helps investors choose stocks that match their risk appetite, optimize returns, and minimize losses. So, what is the Beta coefficient in stock investing? How is Beta calculated? What is its significance and application? Let’s explore the details below with Tipstrade.org!
What is the beta coefficient?
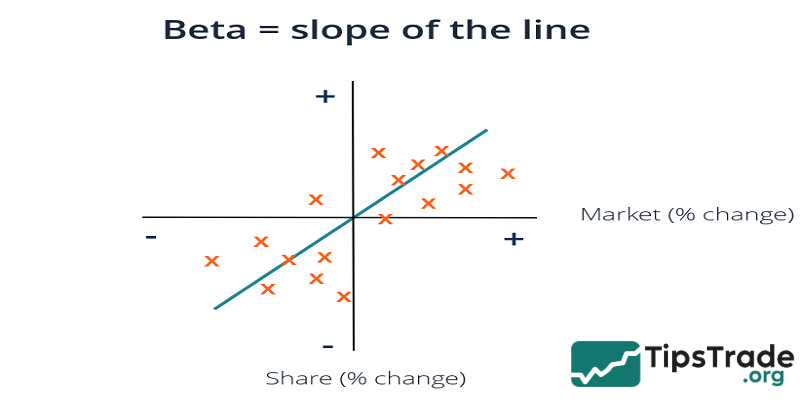
The Beta coefficient (β) in the field of stock investing is understood as a measure of the volatility and systematic risk of a specific security or an investment portfolio compared to the overall market.
The Beta coefficient is used in the CAPM (Capital Asset Pricing Model) to calculate the expected rate of return of an asset based on the market rate of return and its beta value.
>>See more:
Formula to calculate the beta coefficient
The beta coefficient is calculated using the following formula:
Beta coefficient (β) = Cov (Ri, Rm) / Var (Rm)
Where:
- Ri: Rate of return of the stock
- Rm: Rate of return of the overall market (for example in the Vietnamese market, this is the VNIndex)
- Var (Rm): Variance of the market rate of return
- Cov (Ri, Rm): Covariance between the rate of return of the stock (or investment portfolio) and the market rate of return
How to calculate the rate of return R:
R = (P1 – P0) / P0
Where:
- P0: The reference price on the calculation day
- P1: The adjusted closing price of the trading session being measured
In practice, investors do not need to calculate the beta (β) themselves because all the information is readily available on the websites of securities companies. The results may differ across platforms due to varying chosen timeframes. Investors may calculate the average of these values to obtain the most approximate figure.
Interpreting the beta coefficient
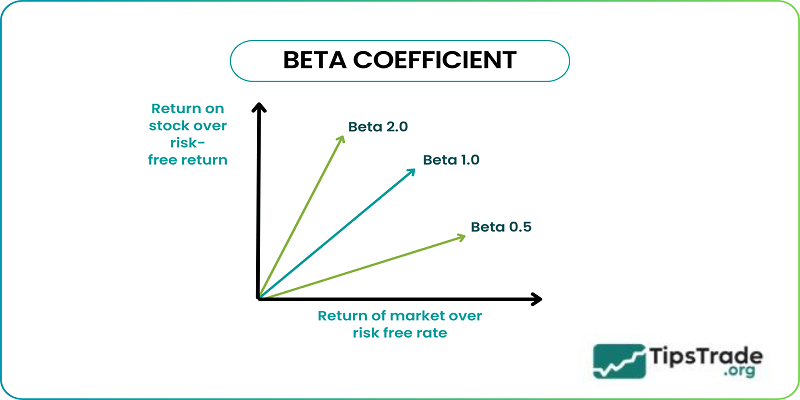
- Beta = 1.0: If a stock has a beta of 1.0, this indicates that its price moves closely in line with the market. The stock carries systematic risk but does not add extra risk to a portfolio, nor does it enhance the potential for exceptional returns.
- Beta < 1: A beta lower than 1.0 indicates that the stock is less volatile than the market, reducing overall portfolio risk. For example, utility stocks often have low betas and fluctuate more slowly than the broader market.
- Beta > 1: A beta higher than 1.0 indicates that the stock is likely to be more volatile than the market. Technology stocks and small-cap stocks often have higher betas, increasing risk but also offering the potential for higher returns.
- Negative Beta: Some stocks have negative beta values, typically showing an inverse correlation with the market. For example, put options and inverse ETFs are often designed with negative beta.
How to apply the beta coefficient in stock investing
Below are the top 6 applications of the beta coefficient in the stock market:
| Application | Description |
| Assessing Investment Risk |
Beta indicates how much a stock or portfolio fluctuates compared to the overall market. • Beta > 1.0: The stock or portfolio is more volatile than the market. • Beta < 1.0: The stock or portfolio is less volatile than the market. |
| Determining Investment Strategy | If you want to invest in stocks with lower risk than the market, you can choose stocks with a low beta. Conversely, if you seek higher return potential (with higher risk), you may choose stocks with a high beta. |
| Selecting Stocks for Investment Funds | Investment funds, such as mutual funds or pension funds, use beta to select stocks for their portfolios. This helps ensure that the portfolio aligns with the investment objectives and risk levels of their investors. |
| Stock Valuation | When analyzing stocks and forecasting future values, investors often use beta to calculate the cost of capital and adjust the present value of a stock. |
| Forecasting Financial Performance | For publicly listed companies, their beta can help predict the impact of market fluctuations on the company’s future profitability. |
Some disadvantages of the beta coefficient in investing
- According to Beta theory, rates of return are assumed to follow a normal distribution, while the stock market is constantly volatile. Therefore, predicting stock prices is not always accurate.
- Since Beta is determined based on past price movements, it cannot accurately assess newly established companies or those issuing shares for the first time.
- The Beta coefficient is only useful for forecasting short-term volatility trends and cannot predict future risks associated with a stock.
- Beta may change over time due to factors such as economic or political conditions.
- Beta is only one factor to consider; investors should also combine it with corporate financial reports or other technical indicators to make well-informed investment decisions.

What is considered a good beta coefficient for a stock?
If you want to invest in line with the overall market, a beta of 1.0 is the ideal choice. A beta lower than 1.0 indicates a lower level of risk compared to the market, making it suitable for conservative investors. Determine the level of risk you are willing to take and your investment goals. A low beta supports capital preservation, while a high beta may deliver higher returns but comes with greater risk.
In a bullish market, a beta greater than 1.0 can generate higher returns than the overall market. However, in a bearish market, a high beta also carries a higher risk of significant losses.
Final thoughts
In conclusion, through the above article, readers have gained an understanding of what the Beta coefficient is in the stock market. Beta is a useful tool for investors; however, it is not the only factor that determines the success of an investment. Investors should combine it with other elements such as fundamental analysis and technical analysis to make well-informed investment decisions.
See more:

