Stock liquidity is a familiar term, but not everyone fully understands its meaning or knows how to accurately assess the liquidity of an asset. In this article, let’s delve into the details of what stock liquidity is, as well as its meaning and how to measure its effectiveness.
What is stock liquidity?
In the financial markets, Liquidity is the ability of an asset to be converted into cash. Convertibility is measured by two components:
- Fast/slow transition time (conversion speed).
- The low loss of value when converted into money.
Stock liquidity is the ability to convert securities assets such as stocks, bonds, fund certificates… into cash and vice versa from cash to stocks. The stock market is classified as one of the markets with relatively high liquidity, easy to buy and sell, and relatively stable prices over time.

>>Read more:
- Stock Issuance: A Detailed A-to-Z Guide for Investors
- What are stock exchanges and how do they work?
- Understanding Dividend stocks and how to invest in them
- What Is Stock Valuation? Notes When Valuation Of Stocks
Characteristics of stock liquidity
- Each stock listed on the stock market has different liquidity.
- Investing in a highly liquid stock is safer than investing in a low-liquidity stock.
- Highly liquid stocks are easy to buy and sell at any time and retain their value (depreciating little).
- Low-liquidity stocks are often in a state of undersupply or oversupply and can be difficult to sell quickly.

How to measure stock liquidity
To determine whether a stock is highly liquid or not, investors often rely on the following criteria:
- Trading volume: A stock with a high trading volume at each price level means that investors can easily buy or sell the stock without significantly affecting the market price. This means that the stock has good liquidity due to its fast turnover rate. A stock is considered to have high liquidity if the average trading volume is above 100,000 shares per session.
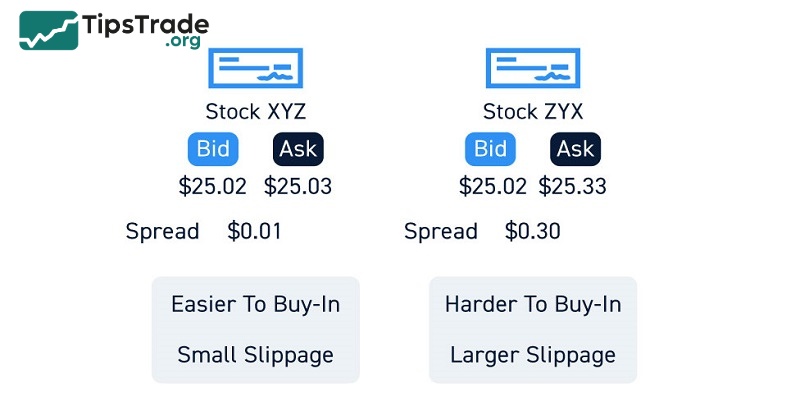
- Difference between buying and selling price: The smaller the gap between the price that buyers are willing to pay and the price that sellers are willing to accept, the more liquid the stock is. Conversely, if this gap is large, the stock will be considered illiquid.
Why stock liquidity matters to investors
Determining the stock liquidity can be considered as one of the important guiding factors for stock investors:
- Reflecting market health: An active and efficient market is one that is highly liquid and has low risk.
- Ensuring easy transactions: Stocks with good liquidity allow investors to buy and sell conveniently.
- Portfolio optimization: Understanding liquidity helps investors make reasonable decisions to optimize investment efficiency.
- Determine stock value: Highly liquid stocks mean that there are many people buying and selling, the stock price is updated frequently and reflects the true value of the stock.
Factors that affect stock liquidity
The factors affecting stock liquidity can be divided into three main groups: internal market factors, external factors, and investor psychology factors.
Internal market factors
- Market size: Large markets increase trading volume and liquidity, while reducing price volatility when trading large volumes.
- Market Depth: Diversity in buying and selling prices supports better liquidity.
- Transparency: Transparent markets increase investor confidence, thereby promoting trading and improving liquidity.
- Corporate Health: Enterprises with good business results are always attractive to investors, so their stocks also have higher liquidity and vice versa.

External factors
- Macroeconomic situation: Factors such as inflation, interest rates and GDP growth directly affect investment decisions, impacting market liquidity.
- Government policy: Monetary policy and tax regulations, foreign investor ownership limits can change trading volume, affecting liquidity.
Investor psychology factors
- Trust the market: A booming market promotes transactions and increases liquidity. On the contrary, a cautious sentiment when the market is in a downward correction will reduce transactions.
- Capital flow from investors: Short-term investors tend to trade more actively but are more susceptible to FOMO (fear of missing out), while long-term investors tend to trade less but help maintain stable liquidity.

How to manage the liquidity risk of stocks
First, let’s learn about the causes of stock liquidity risk.
It can be seen that products on the market such as real estate, gold, insurance,… are all interconnected. Therefore, when the market fluctuates, it will affect the stock market as a whole. That is the cause of liquidity risk in stocks.
The most optimal way to manage liquidity risk is for investors to carefully consider the resale ability of the securities they choose. This will help investors preserve their initial investment capital. This method not only helps investors avoid liquidity risk, prevent the risk of not being able to resell, but also not worry about losing stock value when selling.
In short, investors need to research carefully to allocate their capital appropriately to limit stock liquidity risks.

Notes when investing in low-liquidity stocks
In fact, low liquidity of stocks does not mean that the code is of poor quality, but it may be because the market has not yet recognized the true potential of the company.
But to be safer, when investing in low liquidity stocks you should note the following:
- Research thoroughly: Low liquidity stocks are often issued by small or newly established companies. If you want to invest in these stocks, you should carefully analyze information about the business, consider the potential and profitability of the stock in the future.
- Accept the risk: Low liquidity stocks are often volatile and can be manipulated by groups, causing prices to rise, creating FOMO for inexperienced people. Therefore, you need to prepare knowledge and accept risks when buying this type of stock.
- Split investment capital: Low liquidity will make it difficult to sell stocks when you need cash. Therefore, you should only invest a small amount of capital in low liquidity stocks and prioritize using idle money to invest in this case to minimize risks.
Conclusion
Stock liquidity is the most important factor that you need to analyze when choosing to buy stocks. Prioritize highly liquid codes so you can easily convert them to cash when needed or quickly cut your losses if the market declines, thereby limiting losses when investing in stocks.

