ROE is a very important business metric that anyone interested in economics should understand. In this article, Tipstrade.org will provide a clear explanation of what ROE is, its calculation formula, and what ROE is considered reasonable.
What is ROE?
ROE, short for Return on Equity, is a financial metric that reflects a company’s profitability relative to its shareholders’ equity. In other words, ROE indicates how much profit is generated for every dollar of equity invested in the company. It measures the percentage of net income a company produces compared to its total shareholders’ equity, showing how much profit the company earns from each unit of equity invested.
Return on Equity is considered a “comprehensive” index because it incorporates elements from both the income statement and the balance sheet, reflecting not only profitability but also how the equity is managed. This metric is very useful for assessing a company’s management efficiency, as well as for comparing performance among companies within the same industry.

>>See more:
- What is the Current Ratio? Formula and Examples
- Quick Ratio Explained With Formula and Examples
- Debt-to-Equity (D/E) Ratio Formula and How to Interpret It
- What are Liquidity Ratios? 3 Liquidity Ratios You Should Know
Formula to calculate ROE
Now that you know ROE meaning, let’s understand the ROE formula:
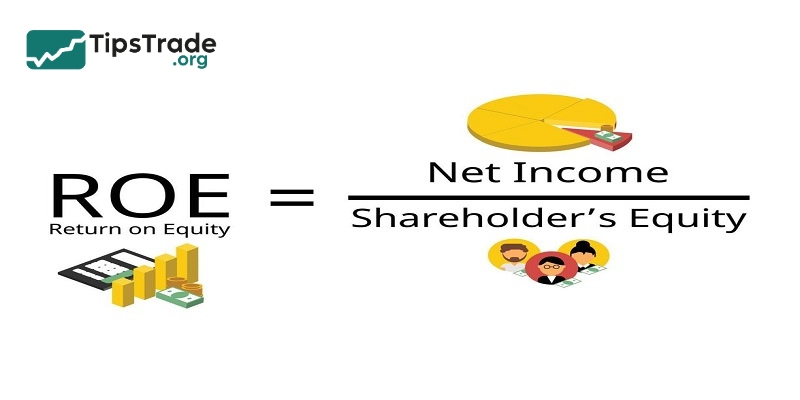
Return on Equity (ROE) = (Net income / Shareholders’ equity) x 100
Where:
- Net income: The company’s total earnings for the period after subtracting all expenses, taxes, and interest. It is found on the income statement.
- Shareholders’ equity: The net worth of the company, calculated as total assets minus total liabilities. It is found on the balance sheet.
Say your company has the following figures:
- Net income = $500,000
- Shareholders’ equity = $2,500,000
Applying the Return on Equity formula:
($500,000 / $2,500,000) x 100 = 20%
This means that for every dollar the shareholders have invested in the company, $0.20 in revenue is generated.
Why is ROE important to understand?
The Return on Equity is a crucial metric as it reflects the financial health of a business. By looking at Return on Equity, investors can understand how much profit is generated from each dollar of equity invested.
- If this metric is positive, it indicates that the company is profitable.
- Conversely, a negative ROE means the company is operating at a loss.

A high ROE suggests that the company has strong growth potential, and investors may consider including its stock in their investment portfolio.
For businesses, ROE is also an important index. A high ROE shows that the company is performing well and that management can continue its current business strategy. On the other hand, a low ROE signals that management should review and adjust the business strategy to achieve better efficiency and results.
What is ideal ROE?
Before evaluating the Return on Equity, investors need to consider the industry in which the company operates. Each sector has its own characteristics regarding capital requirements, operating costs, and profit margins, leading to significant differences in average Return on Equity levels. Therefore, rather than focusing on a single fixed number, investors should compare a company’s ROE with the industry average to gain a more accurate perspective.

Generally, a company with a Return on Equity of 14% or higher is considered to be using its capital efficiently. If the Return on Equity is below 10%, it may indicate that the company is struggling to generate profit from its equity, and investors should exercise caution when considering an investment.
An “ideal” ROE typically ranges from 20% to 22%, signaling that the company is highly profitable and effectively utilizing its capital. However, a high Return on Equity should also be assessed alongside other factors such as debt levels, financial policies, and market conditions to avoid potential investment risks.
Notes when the ROE index is too high
With the above content, you can see the importance of the Return on Equity index, but this index is not always high is a good thing. If a business has a large net profit compared to equity, this can indicate efficient business operations, but it can also be a sign of equity being too small compared to net income, creating a risk factor.
Causes of excessive ROE may include inconsistent earnings where a company has years of losses and then profits, resulting in lower equity but a high Return on Equity. Additionally, high debt and negative net income can also artificially increase the Return on Equity. These situations require careful consideration and calculation on the part of the investor to understand the reasons and risks behind a negative or excessive ROE.

How to apply the ROE ratio to investment
Calculate the growth rate of the business
The growth rate of a company largely depends on its profitability:
Growth rate (g) = ROE x Reinvestment rate
Each year, a company pays a portion of its profits as dividends to shareholders. The remaining profits are reinvested back into the business operations.
Reinvestment rate (%) = (1 – Dividend payment rate)

Example: Companies X and Y both have an ROE of 15%. Company X pays annual dividends at a rate of 25%, while Company Y pays only 10%. The results are:
- Growth rate of X = 15% × (1 – 25%) = 11.25%
- Growth rate of Y = 15% × (1 – 10%) = 13.5%
Although Company X has a higher dividend payout ratio than Company Y, based on the calculation formula, Company Y is expected to have a higher growth rate in the future. In the long term, Company Y’s stock may become more attractive than Company X’s.
Evaluate the ability to create profitability
Evaluating a company’s ability to generate value for shareholders based on the efficiency of capital usage is an important aspect in determining the returns that shareholders can expect. Typically, to assess the value creation for shareholders, Return on Equity is compared with the expected return when purchasing the company’s shares (i.e., the cost of equity). This can be interpreted in the following cases:
- Return on Equity is lower than the cost of equity: This indicates that the company is operating inefficiently, and profits are gradually falling short of initial expectations.
- Return on Equity is higher than the cost of equity: This suggests that the company is performing well, effectively reinvesting earnings, and generating value that exceeds initial expectations.

Identifying the competitive advantages of the business
Typically, leading companies have advantages in production scale and technology, which allows them to achieve lower cost of goods sold per unit. In addition, companies with strong brands can set higher prices compared to competitors in the same industry.
As a result, both profitability and Return on Equity for these companies are often above the industry average. It is crucial for investors to recognize companies with sustainable competitive advantages, as this plays a key role in the potential success of their investments.
Factors affecting the ROE
To adjust the ROE index, a business needs to influence one of the following three main factors:
- Net profit margin is an indicator that shows how much profit is generated from each dollar of revenue. An increase in this indicator shows that the business is operating effectively, has a competitive advantage, and can therefore increase selling prices or reduce production costs.
- Asset turnover measures how efficiently a company uses its assets. An increase in this ratio indicates that the company is generating more revenue from its available assets.
- An increase in financial leverage means that the business is using more external capital sources for production and business.
Drawbacks of ROE
It can be seen that the Return on Equity index is too high sometimes is not a good sign. Therefore, in the process of learning what ROE is, you need to pay attention to the limitations of this index. Return on Equity can also be distorted and changed due to many factors such as long-term losses, large debts, buybacks of shares, …
Another limitation is that Return on Equity may exclude intangible assets from shareholders’ equity. That is, non-monetary items such as patents, trademarks, copyrights. Thus, Return on Equity will be misleading, making it difficult to compare with companies that also include intangible assets.
Each investor calculates a different ROE index because they use different components in the formula: using average equity for two periods, beginning period, end period, etc. This leads to inconsistency and different investment decisions for each trader.
Comparing ROE and ROA: Which metric is more important for investing?
ROA (Return on Assets) measures a company’s profitability based on its total assets, reflecting how effectively a company generates profit from all the resources it owns. Compared to ROE, ROA is also a metric used to evaluate the efficiency of a company’s use of capital and assets, and it is commonly used to compare the performance of companies within the same industry.
However, ROA differs from ROE in several ways:
|
Criteria |
ROE |
ROA |
|
Scope of measurement |
Measures profit based on shareholders’ equity (capital contributed by shareholders). |
Assesses profit based on total assets (including debt). |
|
Impact of debt |
ROE can be inflated if the company has high debt. |
ROA provides a more accurate reflection of profitability from assets. |
|
Significance for investors |
Important for shareholders as it shows the profitability of their invested capital. |
Helps evaluate overall performance, especially how efficiently assets are used to generate profit. |
So, which metric is more important for investing? In reality, neither is universally more important; each should be assessed in specific contexts:
- For companies with high financial leverage (large debt): ROE may be inflated, while ROA will more accurately reflect true operational efficiency.
- For companies with low debt: ROE and ROA are generally similar, and ROE can serve as the primary evaluation metric.
- For long-term investors: ROA is more useful for assessing a company’s sustainability.
- For short-term investors or those focused on shareholder returns: ROE is key for evaluating the profitability of invested capital.
Conclusion
Here is the information about the ROE index that Tipstrade.org has compiled and sent to readers. Hopefully, with the information provided above, you have gained some useful knowledge to make informed and effective investment decisions!
See more:

