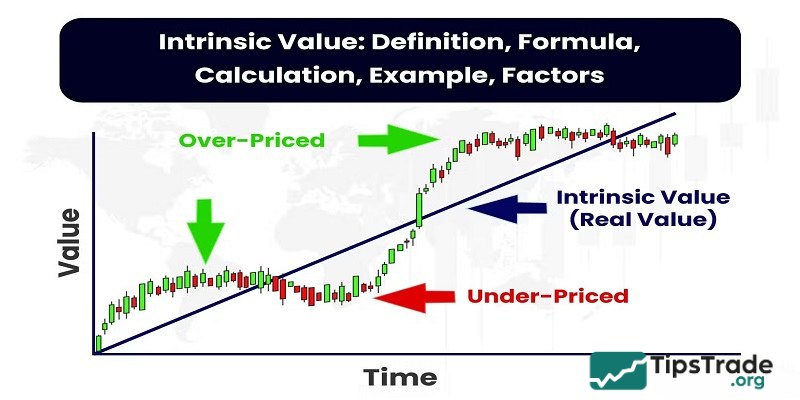
The intrinsic value of a company is one of the key factors when conducting fundamental analysis of a company. So, let’s learn about the term “Intrinsic Value” with Tipstrade.org in the following article.
What is intrinsic value?
Intrinsic value is used to talk about the real value, originating from within the enterprise, different from the book value or market price of the stock. Intrinsic value is also understood as the potential of the enterprise, as well as the driving force of the stock price increase. “Intrinsic” are values originating from the enterprise itself, not affected by factors from the outside market.
The value of a stock on the stock market does not reflect the entire real value of that business. By understanding the real value of the stock, investors can receive long-term benefits.
>>See more:
- What is Industry Comparison and How to do it?
- What are Profitability Ratios? Types & Its Significance
- Key Stock Valuation Ratios and When to Use Which One
- How to Read Financial Statements Like a Pro in Stock Investment
How to calculate intrinsic value
Below, Tipstrade.org will introduce you to 4 popular methods commonly used by fundamental analysts to determine the real value of a stock:
Discounted cash flow (DCF) model
Some economists believe that discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis is the best way to determine the real value of a stock. To perform a DCF analysis, you need to follow these three steps:
- Estimate all of a company’s future cash flows.
- Calculate the present value of each of these future cash flows.
- Sum up the present values to obtain the intrinsic value of the stock.
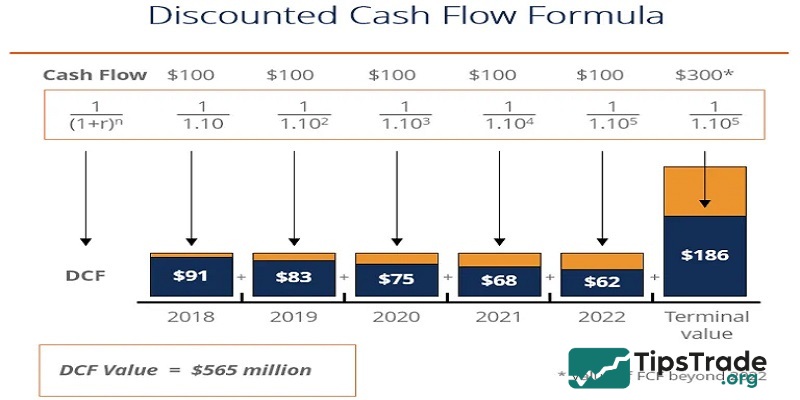
Here’s the formula you can use to calculate the real value of a stock using discounted cash flow analysis:
Intrinsic value = (CF1)/(1 + r)^1 + (CF2)/(1 + r)^2 + (CF3)/(1 + r)^3 + … + (CFn)/(1 + r)^n
Where:
- CF1 is cash flow in year 1, CF2 is cash flow in year 2, etc.
- r is the rate of return you could get by investing money elsewhere
Example: Let’s assume the following projected cash flows for Company XYZ over the next five years:
- Year 1: $10
- Year 2: $12
- Year 3: $15
- Year 4: $18
- Year 5: $20
Assuming a discount rate of 10%, the intrinsic value can be calculated as follows:
Intrinsic Value = (10 / (1 + 0.10)^1) + (12 / (1 + 0.10)^2) + (15 / (1 + 0.10)^3) + (18 / (1 + 0.10)^4) + (20 / (1 + 0.10)^5) = $56.50
According to the DCF method, the estimated intrinsic value of XYZ stock would be approximately $56.50.
=> Since XYZ’s current stock price is $52.00, this suggests that if the intrinsic value represents the true worth of the stock, it is potentially undervalued and may present an investment opportunity.
Dividend discount model (DDM)
This model estimates the intrinsic value of a stock by calculating the present value of expected future cash flows. This process involves projecting future cash flows and discounting them to present value using a certain discount rate.
The main advantage of the DCF model is that it takes into account the time value of money and can be applied to any company with positive cash flows. However, the model is heavily dependent on assumptions and is sensitive to changes in discount rates and growth rates.
The intrinsic value formula in this case is: Intrinsic Value = D1 / (r – g)
Where:
- D1 represents the expected dividend in the next period
- r represents the required rate of return
- g represents the expected dividend growth rate
Example: Assuming an expected dividend of Company ABC is $2.50, a required rate of return of 8%, and a dividend growth rate of 5%, the intrinsic value can be calculated as follows:
Given the following values:
- Expected dividend (D1) = $2.50
- Required rate of return (r) = 8% or 0.08
- Dividend growth rate (g) = 5% or 0.05
=> The real value of a stock = $2.50 / (0.08 – 0.05) = $2.50 / 0.03 = $83.33
=> According to the Dividend Discount Model, the estimated intrinsic value of ABC stock would be approximately $83.33.
Asset-based valuation
The third option is to use the asset-based valuation method to calculate the real value of a stock. The formula for calculating the real value of a stock using this method is perhaps the simplest of all the methods:
Intrinsic Value = Company Assets – Company Liabilities
A company’s assets include both tangible and intangible assets, while liabilities include debts or similar financial obligations.
The limitation of this type of intrinsic value is that it does not take into account the growth potential of the business, which often results in an undervaluation.

Analysis based on a financial metric
This method uses the current stock value and the company’s fundamentals such as revenue, net income, profit, book value, total outstanding shares, etc. Using different financial ratios helps to evaluate the business’s performance. From there, it provides the most comprehensive and accurate view of financial health.
The key ratios used to determine the true worth of the stock are:
- Price-to-book ratio
- Price-to-earnings ratio
- Price to growth ratio
- Return on equity
- Debt to equity
Formula for calculating the true worth of stock according to financial metrics:
Intrinsic Value = Earnings Per Share (EPS) x (1 + r) x P/E Ratio
Where:
- EPS: Earnings per share
- r: rate of return that can be received on investment
- P/E: price-to-earnings ratio.
Why calculating intrinsic value is useful
Stock prices fluctuate around their intrinsic value, but at certain times, the market price can be higher or lower than the intrinsic value, the market price is still very closely linked to the real value of a stock. From there we can see the importance of determining the real value of a stock.
- For investors:
The main objective of calculating the real value of a stock is to determine whether a company’s stock price is undervalued, fairly valued, or overvalued relative to its current market price.
If the stock price is lower than the real value of a stock, investors will try to accumulate more shares to wait for the price to increase and return to its real value. On the other hand, whether the company’s stock price is overvalued or not. This helps investors consider whether to hold the stock or sell for profit.

- For businesses:
Determining the real value of a stock is one of the important and necessary steps for a joint stock company when it wants to raise capital, offer shares, IPO or increase the company’s influence on the stock market.
Factors affecting intrinsic value
The real value of a stock is influenced by many factors, including:
- Business results: A company with good business results demonstrates efficient operations and good management capabilities. High profits help businesses pay off debts and maintain capital, laying the foundation for sustainable development.
- Intangible value: Includes factors such as brand, reputation, human resources, and innovation. These factors are difficult to quantify but play a crucial role in the intrinsic value of a business.
- Market conditions: During periods of economic instability, intrinsic value can be reduced due to market risks and volatility.
- Cash flow: Strong cash flow provides financial stability, supporting investment and expansion activities.

Difference between market value and intrinsic value of stocks
Both market value and intrinsic values are a way of evaluating a company, but there is a significant difference between the two.
| Parameter | Intrinsic Value | Market Value |
| Definition | Actual value of the company, and does not depend on the share price | It is represented the current share price |
| The asset is undervalued and should be purchased when | Higher | Lower |
| The asset is overvalued and should be sold when | Lower | Higher |
| Valuation is correct | Intrinsic value = market value | Intrinsic value = market value |
Conclusion
Intrinsic value is very important in determining the value of a stock for investment purposes. Hopefully, this article has helped investors understand what intrinsic value is and the methods for determining a company’s intrinsic value. Don’t forget to follow Tipstrade.org for more useful knowledge updates!
See more: