Industry comparison is one of the important steps in the process of investing in stocks. It helps investors understand a specific industry, thereby assessing the development potential and choosing potential stocks. So, what is industry comparison and how to do it? Let’s find out with Tipstrade.org through the following article.
What is industry comparison?
Industry comparison is a process that involves quantitative and qualitative assessment of the industry in which a business operates. Industry comparison is a part of fundamental analysis stocks, focusing on various aspects of the industry such as the general situation, legal framework, performance indicators, current trends and future growth potential.
Besides that, industry analysis also helps identify underperforming or outperforming industries, including those with growth potential or those that are stabilizing. In addition to potential investors, industry analysis is also routinely conducted by government agencies, businesses, and market analysts.

>>See more:
- Key Stock Valuation Ratios and When to Use Which One
- What affects stock prices? Key factors every investors should know
- Technical Analysis Stock Trading: A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Everything You Need to Know About Capital Raising in Stock Market
Importance of industry comparison
As mentioned in the above content, industry comparison is an important part of the fundamental analysis of stocks. The importance of industry comparison is shown through the following points:
- Industry comparison helps investors understand the performance of a particular sector in the market.
- It shows whether the industry is growing, contracting or remaining stable, thereby helping to make more accurate investment decisions.
- Investors can better understand the risks and challenges the industry may face in the future.
- Industry comparison provides information about the major companies in that field and the level of competition between businesses.
- It helps investors choose industries with good growth potential in the future and stay away from industries with weak or declining prospects.
- Industry comparison also helps identify the impact of government policies, economic conditions, or global events on the industry.
- It helps minimize the risk of loss by warning about industries that are highly seasonal, risky, or unstable.
- Sector analysis allows investors to compare different sectors and choose the most suitable one based on their goals and risk tolerance.
- Finally, it supports building a solid investment strategy by focusing on industries with long-term growth potential, thereby increasing the chances of achieving high returns through investing in areas that perform well.

What are the aspects of industry comparison?
There are various aspects to analysing an industry to understand its strengths and weaknesses and potential investment opportunities. Some of the broad aspects to be covered under industry comparison are explained below.
Industry overview
Industries, like businesses, typically go through a series of stages, from formation to growth to maturity and finally decline.
Determining which stage of the life cycle an industry is in helps us see the level of competition as well as the revenue and profit prospects of businesses in the industry.
It is therefore necessary to determine the current stage in the industry’s life cycle:
Emerging? (very new industry, growing less than 5% a year)
- Growing? (slow growth phase at a rate slightly greater than 5% per year)
- Turbulence? (a stage of development in which companies merge or consolidate and/or some companies fail)
- Mature? (growth slows down, below 5% a year)
- Decline? (a stage where there is no growth for a long period of time)
Trends and developments
For this aspect in industry comparison, investors need to determine how the industry scale has changed over the years? In the next 5 years, 10 years? The expected development of the related industry? Analyze the factors affecting the development of the industry including:
- The New Demographic Shift Affects the Industry
- Competition from rival companies
- Customer taste trends
- The impact of globalization and technological innovation.
- The legal environment and economic realities at global, national and local levels also need to be taken into account.

Barriers to industry entry or expansion
Barriers can be in the form of market competition and can also manifest in financial or human resource shortages, legal restrictions and copyrights.
For example, if you plan to enter or expand the microchip production line, you will need to invest tens of billions of dollars in machinery and equipment. Moreover, you will need computer engineers and programmers to produce and design.
Competition from other firms in the industry will not only be for customers but also for human resources. All of these need to be considered when considering barriers to entry into the industry.
Competition in the industry
Providing a description of the major competitors in the industry is very important in industry analysis. So what exactly does this mean in industry comparison?
Use detailed statistical information on revenue, human resource and product strengths. Their past business decisions, upcoming products and marketing strategies. Includes analysis of sourcing, manufacturing and legal.
Company analysis should be as comprehensive as possible. Competitive advantages and disadvantages can appear from all sides.
- Are your competitors using large billboards? How many of each type are effective? Consider whether your company can match or compete with them in terms of marketing.
- Look at recent innovations or mistakes your competitors have made. Learn from their failures and build on their successes.

Position your company in the industry
Information about the competitive landscape, barriers to entry or expansion, industry trends and available customer attention, how the company is positioned within the industry and compared to other competitors. Include statistical information about your business and be honest about the advantages and disadvantages the company will face.
How to conduct industry comparison?
There are many ways in which you can do this. However, we have zeroed down some of the best methods below to help you industry comparison:
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
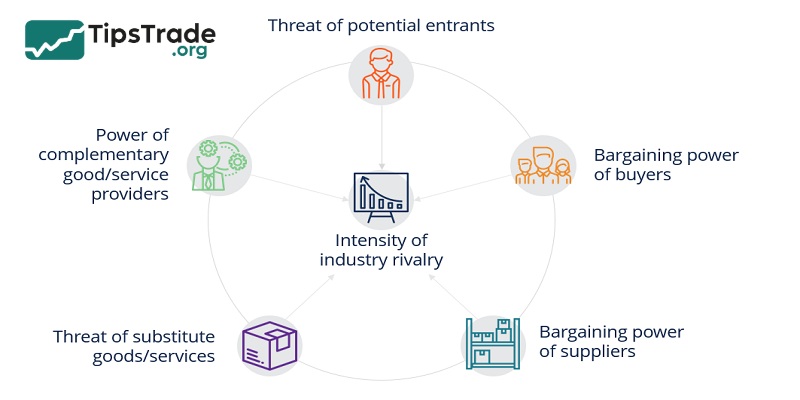
One of the most famous models ever developed for industry comparison is Porter’s 5 Forces Model, introduced by Michael Porter in his 1980 book “Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors”.
According to Porter, analyzing the five competitive forces helps to accurately reflect the situation of an industry and makes the analysis process easier. Here are the five forces:
- Threat of new entrants – Can new companies easily enter the industry?
- Bargaining power of suppliers – Do suppliers have control over prices or supply?
- Bargaining power of customers – Can customers demand better prices or quality?
- Threat of substitutes – Are there other products that can replace what the industry offers?
- Industry rivalry – How intense is the competition between existing companies?
PESTEL Analysis
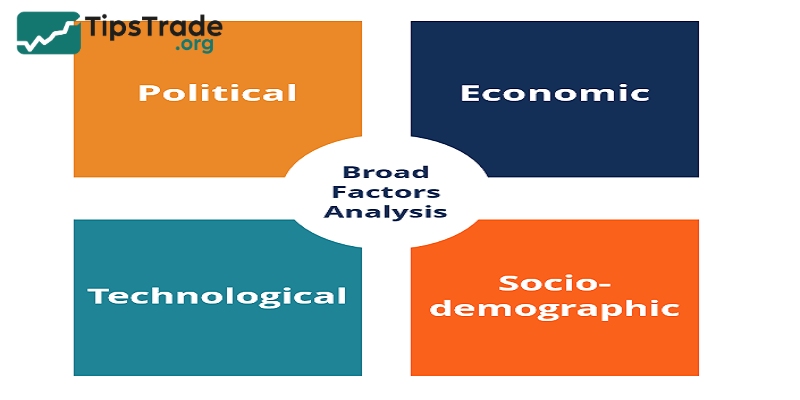
PEST Analysis stands for Political, Economic, Social and Technological. This method is a useful framework for analyzing the external environment.
To use PEST as a form of industry comparison, an analyst will analyze each of the 4 components of the model. These components include:
Political factors include government policies, tax rules, and trade regulations.
- Economic factors include inflation, interest rates, and GDP growth.
- Social factors involve changes in population, culture, and consumer preferences.
- Technological factors look at innovation, automation, and the use of digital tools.
- Environmental factors deal with climate change, pollution, and sustainability.
- Legal factors involve labour laws, safety standards, and industry regulations.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This method can be a great way of summarizing various industry forces and determining their implications for the business in question.
So if you are running a SWOT analysis on an industry you will have to chart out the:
- Strengths: Factors that give the industry an edge over the others.
- Weaknesses: Factors that keep businesses at a disadvantage.
- Opportunities: Factors present in the economy and external environment that positively impact the performance and profitability.
- Threats: Factors present in the economy and external environment that negatively impact the performance and profitability.

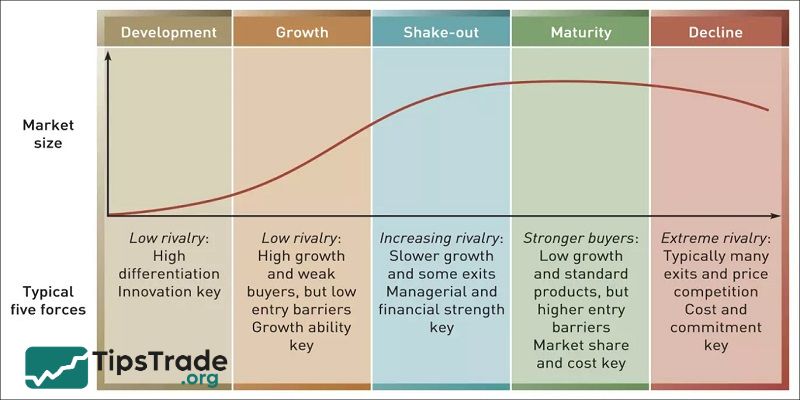
Lifecycle Analysis
Every industry goes through four basic stages, including: Introduction, Growth, Maturity and Decline. This method helps investors determine which stage the industry is in its development cycle.
- In the introduction stage, the industry is new and small.
- The growth stage reflects rising demand, and companies are making good profits.
- The maturity stage shows slow growth, and competition becomes strong.
- In the decline stage, sales drop and the industry may shrink.
Understanding the stage of development of an industry helps investors plan when to enter or exit the market.
Pros and cons of industry comparison
Industry comparison provides an in-depth understanding of the industry in which a company operates, thereby helping investors make more informed and accurate investment decisions. However, it is a complex and time-consuming process that requires a clear understanding of financial data. Below are the pros and cons of conducting industry comparison.
Pros:
- Provides a clearer understanding of industry trends and growth.
- Helps identify potential opportunities and risks.
- Supports making informed investment decisions.
- Helps compare different industries to choose the best one.
- Highlights competitive strengths and weaknesses in a sector.
- Enables forecasting of future market behaviour.
Cons:
- Can be time-consuming and require extensive data gathering.
- May involve complex information that can be hard to interpret for beginners.
- The quality of analysis depends on the accuracy of available data.
- It may not predict sudden changes like political events or natural disasters.
- External factors may suddenly change, making predictions less reliable.
- Sometimes, over-analysis can lead to decision paralysis.
Conclusion
The above article provides extremely detailed information if you want to learn about Industry comparison. Tipstrade.org hopes that this knowledge will be helpful to you on your stock investment journey.
See more:

