What is CFD? CFD trading offers the ability to profit from both rising and falling market conditions. It is considered a popular financial instrument that enables investors to access global markets. However, not everyone fully understands this concept. So, what is CFD? What are its advantages, disadvantages, and how does CFD trading work? Let’s explore these topics in the article below.
What is CFD?
CFD (short for Contracts for Difference) is a type of agreement between two parties that allows investors to profit from the price movements of an asset without actually owning it. Essentially, you are “betting” on whether the price will go up or down. Your profit or loss is determined by the difference between the price at which you open and close a trading position.
To put it simply, instead of buying a stock in the hope that its price will rise, you can trade a CFD on that stock. If you predict that the price will increase and it does, you earn a profit equal to the price increase. Conversely, if the price falls, you incur a loss.

One of the key attractions of what is CFD that they allow you to profit from both rising and falling markets. In addition, CFDs enable the use of leverage, meaning you can control a larger trading position with a relatively small amount of capital. However, leverage is a double-edged sword, as it can amplify both profits and losses.
How does CFD trading work?
What is CFD? CFD trading does not require you to actually own the underlying asset. Instead, you enter into a contract with a broker, where you “bet” on whether the price of that asset will rise or fall. When trading, you decide whether to buy or sell (corresponding to predicting a price increase or decrease), choose the level of leverage, the trade size, and other parameters. Your position remains open until you close it manually or until it reaches the predefined stop-loss or take-profit level.
Your profit or loss is determined by the difference between the opening and closing prices of the position. If your prediction is correct, the broker pays you that price difference. Conversely, if your prediction is wrong, you must pay the price difference to the broker.
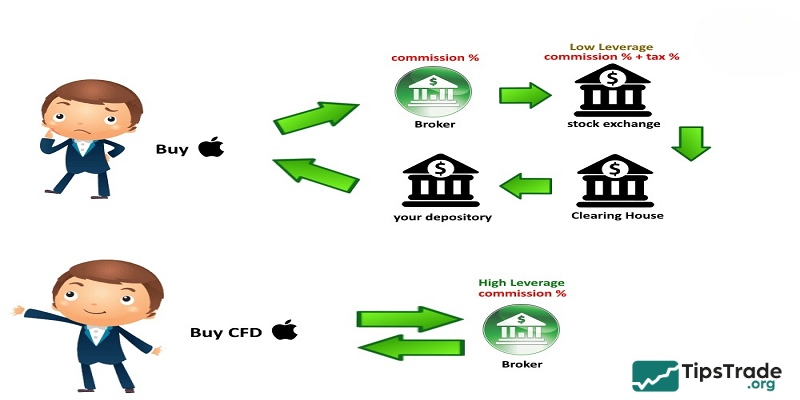
To trade CFDs effectively, you need to understand several key concepts such as spreads (the difference between the bid and ask prices), commissions, trade size (lot), and contract duration. A clear understanding of these factors will help you calculate trading costs and make well-informed investment decisions.
Types of CFD trading
The CFD market is highly dynamic and offers a wide range of trading styles to suit the risk appetite and strategies of different investors. Below are some of the most common approaches:
- Day trading: This is a fast-paced strategy in which traders open and close positions within the same day, sometimes within just a few hours. The main advantage of day trading is that it reduces overnight risk, helping traders avoid unexpected price movements when the market is closed. However, it requires intense focus and the ability to react quickly to market changes.
- Swing trading: With swing trading, traders hold positions for several days to about a week, aiming to profit from short-term market fluctuations. Swing trading provides more opportunities than day trading but also involves overnight risk, as unexpected events may occur while the market is closed.
- Scalping: Scalping is a “quick profit” strategy in which traders execute many trades over a very short period, often just seconds or minutes, to profit from the smallest price movements. Scalping demands high accuracy, speed, and discipline, and typically involves the use of high leverage to maximize returns.
- Long-term trading: This approach is suitable for patient investors with a long-term perspective. Positions are held for several weeks to several months, or even years, based on fundamental analysis of the asset’s underlying value and macroeconomic factors affecting the market. Long-term trading requires deep knowledge and the ability to anticipate future market trends.
Assets you can trade as CFDs
Once you understand what is CFD, you will see that they are a highly flexible trading instrument, allowing you to invest in a wide range of assets without actually owning them. Common asset classes include:
- International stocks: Apple, Google, Tesla, Facebook, Amazon, etc.
- Stock indices: S&P 500, NASDAQ, Dow Jones, UK100, EU50, etc.
- Energy: Crude oil (Brent, WTI), natural gas, etc.
- Precious metals: Gold, silver, copper, aluminum, etc.
Agricultural commodities: Coffee, cotton, corn, cocoa, etc. - Foreign exchange (Forex): EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, USD/CHF, etc.
- Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Ripple (XRP), Litecoin (LTC), etc.

With just a single CFD trading account, you can access and trade hundreds of financial products worldwide, from Wall Street to the cryptocurrency market.
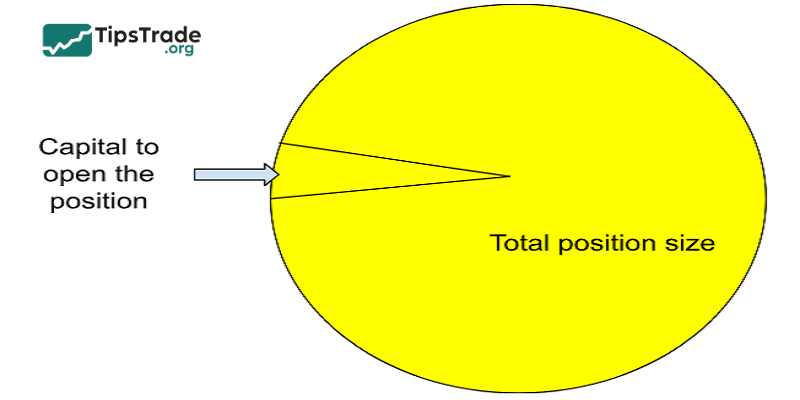
Leverage in CFD trading
What is CFD? In CFD trading, leverage allows you to control a much larger trading position than the amount of capital you actually have. For example, with a margin requirement of 10%, you only need to invest 100 million VND to trade a stock position worth 1 billion VND. The broker lends you the remaining 900 million VND.
This is similar to being able to buy a house worth 1 billion VND with only 100 million VND in cash. Thanks to leverage, you can participate in the market with a relatively small amount of capital and magnify your potential profits.
However, just like borrowing money to buy a house, leverage also comes with risks. If the market moves against your prediction, your losses will be amplified as well. Therefore, using leverage requires careful consideration and should always be combined with effective risk management.
Basic guide to CFD trading
Below are the basic steps to help you get started with CFD trading effectively:
- Step 1 – Learn about CFDs: Understand what CFDs are, how they work, as well as the benefits and risks involved.
- Step 2 – Choose a reputable broker: Select a broker that is licensed by a major financial authority to ensure transparency and trading safety.
- Step 3 – Choose a trading asset: Decide which asset you want to trade, such as forex, stocks, gold, or indices.
- Step 4 – Open an account and deposit funds: Register an account, complete identity verification, and deposit an amount suitable for your financial capacity.
- Step 5 – Choose a position (buy or sell): Predict the price trend and select the appropriate position. You can open a buy order if you expect prices to rise, or a sell order if you expect prices to fall.
- Step 6 – Place a trade: Set trading parameters such as trade size (lot), leverage, stop-loss, and take-profit levels, then place the order.
- Step 7 – Monitor and close the trade: Track market movements and close the position when your target is reached or to limit losses.

Advantages and disadvantages of CFD trading
Advantages of CFD trading
- Flexibility and cost efficiency: You do not need to own the underlying asset, which helps save on storage, custody, and related taxes. Moreover, CFDs allow you to enter the market with a smaller amount of capital thanks to financial leverage.
- Diverse profit opportunities: In addition to profiting from rising prices, you can also make money when prices fall. CFDs enable you to flexibly “bet” on both directions of market movement, increasing profit potential.
- Leverage and low costs: Leverage allows you to control a larger trading volume with limited capital, maximizing potential returns. In addition, CFD trading costs are often lower than those of traditional trading.
- Access to multiple markets: With a single account, you can trade across a wide range of markets, from stocks and indices to forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. This opens up opportunities for investment and effective portfolio diversification.

Disadvantages of CFD trading
- Trading costs: When trading CFDs, you must pay the spread, which is the difference between the buying and selling prices. This means that even if a trade is profitable, part of the profit will be used to cover the spread cost.
- Leverage risk: While leverage allows you to control a larger position with less capital, it also amplifies both gains and losses. If the market moves against your expectations, leverage can cause you to lose your entire invested capital, or even more.
- Higher risk compared to traditional stock trading: CFDs are derivative products and generally carry a higher level of risk than directly buying and holding stocks. Especially when leverage is used, even small market fluctuations can result in significant losses.
Who should trade CFDs?
If you have ever wondered what is CFD and whether they are suitable for you, the answer depends on your goals and your ability to manage risk. Specifically, this form of trading may be suitable for the following individuals:
- Those with basic investment knowledge and the ability to analyze the market.
- Investors who want flexible trading and access to multiple markets.
- Traders with limited capital who are seeking higher profit opportunities.
- Individuals who can tolerate risk and have a clear capital and risk management plan.
On the other hand, if you lack experience or are looking for a safe, long-term investment approach, CFDs may not be the right choice for you.
Conclusion
What is CFD? This is a powerful financial instrument that offers investors opportunities to enhance their profit potential. However, alongside its notable advantages, CFDs also carry certain risks, particularly those associated with leverage. Therefore, before entering the CFD market, investors should equip themselves with solid knowledge, market analysis skills, effective risk management strategies, and a stable trading mindset. We hope this article has provided you with useful insights into CFD trading. Wishing you success on your investment journey!

