What are shares? is one of the fundamental concepts that individual investors often learn about when they begin their journey of understanding stocks in particular and the stock market in general. The following article from Tipstrade.org will provide some general insights and how stocks work for investors to reference.
What are shares?
What are shares? A share is a type of stock issued in certificate form and represents a portion of ownership in a company. When you buy a share of a company’s stock, you become a shareholder, entitled to a share of the company’s profits (if any) and voting rights in important company decisions. The value of a stock often fluctuates according to the company’s business performance, market conditions and other economic factors.

>>Read more:
- How To Buy Stocks in 4 Steps: Quick-Start Guide for Beginners
- Common Stock Risk Management Strategies for Investors
- ETF Investing: The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- Blue Chip vs Penny Stocks: Which is Suitable for You?
How do shares work?
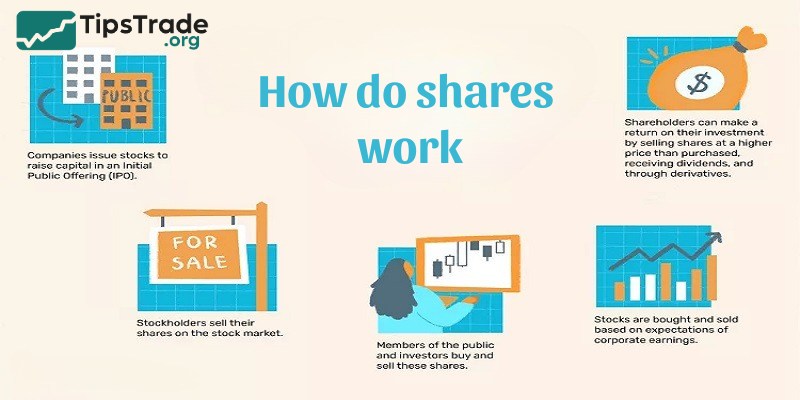
What are shares and how do they work? Shares work by giving investors direct exposure to a company’s performance. Shares will rise in value when the company is doing well, and they’ll fall in value when the company is doing poorly.
Stock exchanges facilitate the exchange of shares in publicly listed companies. There are a few ways for a company to go public, but the more traditional and most common is for the company to hold an initial public offering (IPO).
Types of shares
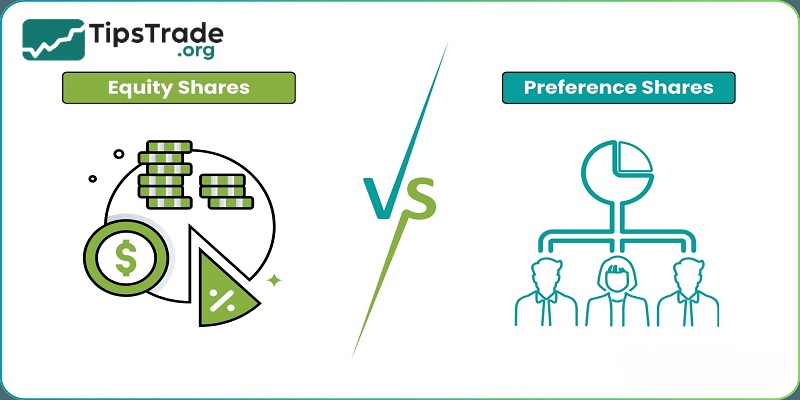
What are shares and how are they divided? To better understand what are shares, you must clearly distinguish between the different types of shares. Specifically, shares are divided into two main types:
Ordinary equity shares
Ordinary shares carry no exceptional or preferred rights. Ordinary shareholders are entitled to share in the earnings of the company. They can vote at the company’s general meeting as well as other official meetings. They are also eligible to participate in any dividends or any distribution of assets on winding up of the company.
Preference shares
Preference shareholders usually get a significance or ‘priority’ over ordinary shareholders in terms of payments of dividends or on winding up of the company. There are varying degrees of preference shares having different rights and characteristics. Holders of preference shares are entitled to having a fixed periodic income and have restricted voting rights liable to particular circumstances or particular resolutions; however this is strictly dependent on the terms of the shares.
>>Read more:
- ADR Stocks: A Complete Guide for Global Investors
- Growth Stocks – Definition, Examples, Characteristics
- Preferred Stock – What It Is, How It Works, and Should You Invest?
- Everything You Need to Know about Sustainable Stocks
Why invest in shares?
What are shares? Why invest in shares? Investing in shares gives investors several benefits in terms of profitability and long-term capital growth. Some of the benefits that investing in shares can bring you are:
- Profit from price difference: Specifically, you profit from the price difference when you buy stocks at a low price and sell them at a high price.
- Capital growth: If the company does well and its value increases, your share price will also increase. This gives your initial investment the opportunity to grow many times over.
- Receive dividends: Dividends are profits that a company distributes to investors on a quarterly or annual basis. So when you buy shares in a company, you get a share of the profits without having to sell the shares.

Risks associated with investing in shares
What are shares? Is investing in shares risky? Besides the attractive profit benefits, investing in shares also has many potential risks that you should consider carefully before participating. Below are some risks when you invest in shares:
- Business risks: You could lose your entire initial investment if the company performs poorly and the stock price plummets and you have to sell the shares for less than you bought them.
- Market volatility: The stock market in general includes many factors such as exchanges, securities companies, investors, which can cause fluctuations in stock prices. Therefore, you may be at risk of losing capital if the stock price drops sharply due to market influences such as economic recession, deflation or inflation,…

Where are shares traded?
What are shares and where are they traded? Shares are traded on stock exchanges. The role of the exchange is to provide a safe and regulated environment where shares can be bought and sold, while also ensuring that listed companies meet strict standards of corporate governance.
Exchange opening times
Stock exchanges are not open 24/7. They have fixed opening and closing hours. Be aware of time zone differences, as you will not be able to trade stocks if the exchange is closed.

New York stock exchange (NYSE)
Open Monday through Friday, 9:30 AM – 4:00 PM (EST)
Founded in 1792, the NYSE is the world’s largest stock exchange by market capitalization – larger than the NASDAQ, the London Stock Exchange and the Tokyo Stock Exchange combined.
Some of the notable companies listed on the exchange include: Alibaba, Johnson & Johnson and Wal-Mart.
NASDAQ
Open Monday through Friday, 9:30 AM – 4:00 PM (EST)
Located in New York, NASDAQ (National Association of Securities Dealers – Automated Quotation System) is the second largest exchange in the world.
This is a technology-focused exchange, which includes big names like: Apple, Amazon, Intel, Cisco, and Microsoft.
London stock exchange (LSE)
Open Monday to Friday, 8:00 AM – 4:40 PM (GMT)
First founded in 1698 as the Royal Exchange, the LSE is Europe’s largest stock exchange.
Listed companies include: Unilever, BP, GlaxoSmithKline, HSBC and Royal Dutch Shell.
Tokyo stock exchange
Open 9:00am – 11:30am, then 12:30pm – 3:00pm (JST)
Founded in 1878, the Tokyo Stock Exchange is the largest in Asia. Notable listed companies include Sony, Toyota and SoftBank.
How to buy and sell shares
After learning what are shares, the question that arises is: how do you buy and sell stocks? Here’s a detailed guide for you:
Buying
- Choose a broker: Selecting a suitable brokerage platform is a critical first step in buying shares. Investors should consider factors such as trading fees, research tools, and the platform’s user-friendliness. Different brokers may also offer varying levels of customer support and educational resources.
- Research stocks: Thorough research is essential before buying shares. Investors should analyse company fundamentals, financial reports, and industry trends. Understanding a company’s competitive position, growth prospects, and potential risks helps investors make informed decisions.
- Place an order: Once research is complete, investors can place an order to buy shares. They can choose from different order types, including market orders (buying at the current market price), limit orders (setting a specific price to buy), and stop orders (triggering a purchase when the stock reaches a predetermined price).
- Pay: After placing an order, investors need to transfer funds to their brokerage account. Most brokers offer various payment methods, including bank transfers and credit/debit card payments.
- Monitor: Successful investing requires ongoing monitoring. Investors should keep track of their investments, staying informed about company news, industry developments, and changes in market conditions. Regular monitoring helps investors make timely adjustments to their portfolios.

Selling
- Decide to sell: Investors may decide to sell shares for various reasons, such as reaching investment goals, taking profits, or responding to changing market conditions. Deciding when to sell requires a careful assessment of the overall investment strategy and market conditions.
- Place an order: When ready to sell, investors can place a sell order, specifying the selling price and order type. Like buying orders, sell orders can be market orders, limit orders, or stop orders.
- Receive payment: Once the sell order is executed, investors receive the proceeds from the sale. The funds are typically deposited into the investor’s brokerage account.
- Evaluate your investment: After selling shares, investors should evaluate the performance of the investment. Reflecting on the reasons for selling, analysing the overall outcome, and reassessing investment goals contribute to continuous learning and improvement in investment strategies.
Tips for new investors
- Research thoroughly: Read the company’s financial statements and industry analysis.
- Diversify your portfolio: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket.
- Patience and discipline: Stock investing is a long-term strategy.
- Using analysis tools: Apply some tools such as P/E, ROE, or in-depth reports from experts.
Conclusion
What are shares? Shares are an attractive investment channel with high profit potential. However, to succeed, you need knowledge, a clear strategy, and a determined spirit. Start with basic learning, small investments, and continuously improve your knowledge. Wishing you successful investments!

