Interest rate forex is a major driver of the forex market. This strong correlation causes forex traders to closely monitor the interest rates of each country involved in the currency pair they are interested in in order to predict the next moves of the currency. So, what is the interest rate forex? How does it affect currency values and the forex market? Let’s find out with Tipstrade.org through the article below!
What is the interest rate forex?
When we talk about interest rate forex, we are not referring to the specific interest rates of a particular bank, but rather we are referring to the monetary policy of a country’s central bank. When interest rate forex are expected to change, the corresponding currency will usually react shortly after it. Central banks have different monetary policy tools to influence interest rate forex as well as currency values.
- What is Forex? The Complete Guide for Beginners
- What are exchange rates? How to read and analyze rates in Forex
- Important Economic Indexes Every Trader Needs To Know
- The Impact of Central Bank vs Forex – Understand to Invest Effectively

List of central banks of major currencies in the forex market:
| Country | Central Bank (Abbreviation) |
| Australia | Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) |
| Canada | Bank of Canada (BOC) |
| European Union | European Central Bank (ECB) |
| Japan | Bank of Japan (BOJ) |
| New Zealand | Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) |
| Switzerland | Swiss National Bank (SNB) |
| United Kingdom | Bank of England (BOE) |
| United States | Federal Reserve (Fed) |
There are two main functions typically performed by central banks, which include:
- Inflation management
- Maintain the country’s exchange rate stable
Interest rates and exchange rates often reflect the health of a particular economy:
- Central banks tend to raise interest rates when the economy is growing, and thus cause inflation.
- On the other hand, cutting interest rates during economic recessions often serves as a means of stimulating a struggling economy.
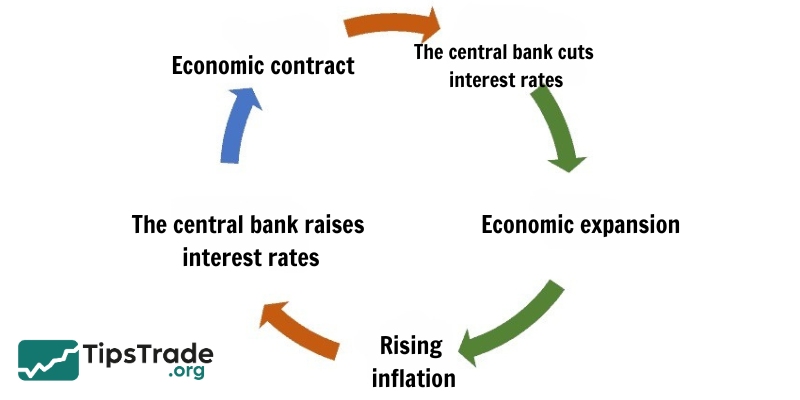
Economies are always in motion, either expanding or contracting. The main goal of central banks is to keep an eye on the inflation rate, allowing the economy to grow steadily. This relationship will be discussed further below.
Understand about economic cycle and interest rates
Economies are always either expanding or contracting. When economies are expanding, things are better. When economies are in recession, things are worse. The goal of central banks is to keep inflation under control. They allow the economy to grow at a modest pace by adjusting interest rates.
When the economy is expanding – GDP growth is positive, consumers earn more money. More income leads to more spending. More money used to buy fewer goods causes inflation. If inflation is left unchecked, it can be disastrous. So central banks try to keep inflation within a 2% limit (for most central banks), by raising interest rates. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive and help reduce spending and inflation.
If the economy is contracting – GDP growth is negative, negative inflation becomes a problem. The central bank lowers interest rates to stimulate spending and investment. Companies start lending money at low interest rates to invest in projects. This increases employment, growth, and eventually inflation.
A typical business cycle looks like this:
Impact of interest rates on Forex
How do interest rates affect the forex market? Interest rates and the forex market – It is through the change in interest rate expectations that the demand for currencies changes. The table below shows the possible scenarios that can occur due to changes in interest rate expectations:
| Market Expectation | Actual Result | FX Impact Result |
| Increase interest rate | Keep interest rate unchanged | Currency depreciates |
| Decrease interest rate | Keep interest rate unchanged | Currency appreciates |
| Keep interest rate unchanged | Increase interest rate | Currency appreciates |
| Keep interest rate unchanged | Decrease interest rate | Currency appreciates |
Finding out the interest rate difference in Forex
The interest rate differential is simply the difference in interest rates between two countries.
If a trader expects the US to unexpectedly raise interest rates, they predict that the US dollar may appreciate. To increase the trader’s chances of success, the trader can buy the US dollar against a currency with a low interest rate. This is because the two currencies diverge in the direction of their respective interest rates.
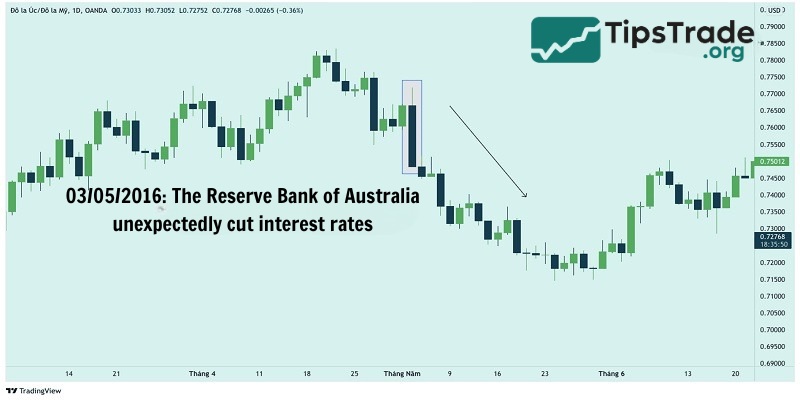
Interest rates and their differentials have a big impact on the appreciation/depreciation of currency pairs. Changes in the interest rate differential are correlated with the appreciation/depreciation of currency pairs. It is easier to understand visually.
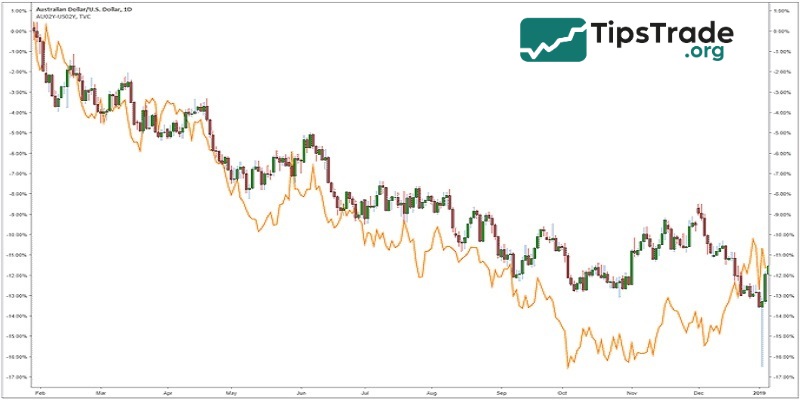
The chart below compares the AUD/USD currency pair (candlestick chart). It also shows the difference between the two-year AUD government bond and the two-year USD government bond (orange indicator). See that as the AUD bond yield falls relative to the USD bond, so does the currency.
Interest rate differentials are widely used in Carry Trade transactions. In a carry trade, money is borrowed from a country with low interest rates. It is then invested in a country with higher interest rates. However, there are risks involved in the carry trade. For example, the currency invested may depreciate relative to the currency used to make the transaction.
How to trade Forex based on interest rates?
Predicting central bank interest rates
Indicators that correlate with how central banks set and change monetary policy include:
- Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- Consumer price index
- Unemployment or employment rate
- Subprime Market
- Housing index
With the data from the above indicators, forex traders can make an estimate of interest rate changes. Typically, when these indicators improve, the economy is doing well and interest rates will need to be raised or if the improvement in these indicators is not significant, interest rates may be kept unchanged. If these indicators decrease significantly, it may signal a rate cut to encourage lending and spending.
In addition to economic indicators, interest rate decisions can be predicted by:
- Follow key announcements
Major announcements from central bank leaders often play a key role in moving interest rates. Whenever the board of directors from any of the eight major central banks is scheduled to make a public announcement, it usually provides insight into how the bank views inflation.
- Interest rate forecast analysis
The second way to predict interest rate forex decisions is by analyzing forecasts. Because interest rate forex moves are often anticipated in advance, brokers, banks, and professional traders will have a consensus estimate of what interest rates will be.
Traders can take four or five of these forecasts and average them for more accurate predictions.
What to do if an unexpected interest rate change occurs?
No matter how good a trader’s research is, central banks always have the ability to make a surprise interest rate forex adjustment up or down.
When this happens, a good trader should know which way the market will move. If interest rates rise, the currency will appreciate, which means other forex traders will buy. If there is a cut, forex traders will likely sell and buy other currencies with higher interest rates. Once you have identified the market movement, it is important to do the following:
- Act fast! The market tends to move at lightning speed when surprises occur as all traders want to buy or sell (depending on whether interest rates are rising or falling) before the crowd. Acting fast can lead to significant profits if done correctly.
- Watch for trend reversals. Trader perception tends to drive the market when data is released, but the trend is likely to reverse and continue in its original direction afterward.
The following example illustrates the action when the market suddenly moves.
In early July 2008, the Reserve Bank of New Zealand was operating at 8.25% – one of the highest rates among central banks. The exchange rate had been stable for the previous four months as the New Zealand dollar was seen as a more profitable investment compared to lower-interest-bearing currencies.
In July, against all expectations, the board of the Bank of New Zealand abruptly cut interest rates to 8% at its monthly meeting. While the percentage cut may seem small, forex traders took it as a sign of the bank’s fear of inflation and immediately withdrew or sold the currency and bought another currency, even though other options offered lower interest rates.
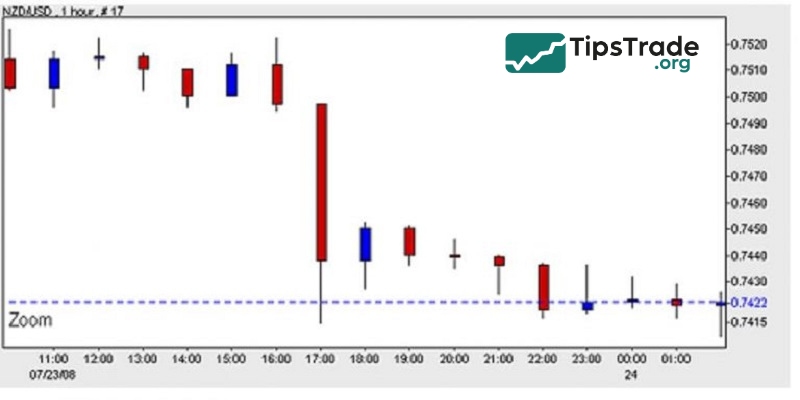
The NZD/USD exchange rate fell as the market reacted to the Bank of New Zealand’s interest rate cut. The NZD/USD exchange rate fell from 0.7497 to 0.714 – a total of 83 pips – in 5 to 10 minutes. Those who sold 1 lot made a net profit of $833 in just a few minutes.
As soon as the NZD/USD volatility subsided, it was not long before the NZD/USD resumed its uptrend. The reason it did not continue to free fall is that despite the rate cut, the NZD still has a higher interest rate (at 8%) than most other currencies.
Conclusion
Interest rate forex is a powerful tool that central banks use to regulate the economy and influence the currency market. For traders, closely monitoring changes and predicting interest rate forex is very important to make the right trading decisions. Recognizing the trends of interest rate policies and understanding how they affect exchange rates will help traders have effective trading strategies and minimize risks. Wish traders success!
>>Read more:

