Stock prices fluctuate constantly, and there is virtually no fixed formula for accurate prediction. But, understanding the impact of macroeconomic factors on stocks will help investors “read” the market better, avoid being swayed by rumors, and make more informed investment decisions. So, which macroeconomic factors impact the stock markets? Let’s learn about it with Tipstrade.org in the article below!
What are macroeconomic factors?
Macroeconomic factors refer to the broad economic elements that influence the overall performance, structure, and behavior of an economy. These factors are not limited to a single company or industry but affect an entire nation’s economic environment.
By analyzing these indicators, economists and investors can gain valuable insights into the direction of the economy, whether it is expanding, stagnating, or entering a recession. Understanding macroeconomic factors is crucial because they serve as the foundation for predicting market movements, investment risks, and business cycles.

>>See more:
- What is bid ask spread? Factors that influence bid ask spread
- Factors Affecting Stock Prices: Key Drivers Behind Share Movements
- Market Cap Stocks: What They Are and Why They Matter for Investors
- What is Stock Liquidity? Why It’s Important for Investors
The connection between economy and stock market
The stock market acts as a mirror of the economy. When the economy grows, companies generally experience higher profits, leading to rising stock prices and increased investor confidence. Conversely, during economic downturns, corporate earnings often decline, prompting investors to sell shares and causing market prices to fall.
Changes in macroeconomic conditions (such as an increase in interest rates or a spike in inflation) can significantly affect how investors perceive risk and opportunity. For instance, higher interest rates may discourage borrowing and reduce business expansion, leading to lower stock valuations. On the other hand, strong GDP growth or favorable fiscal policies can boost market optimism and attract more investments.
In short, macroeconomic factors serve as the driving force behind stock market fluctuations, shaping both short-term investor sentiment and long-term economic trends. Understanding this relationship helps investors make informed decisions and build resilient investment strategies.
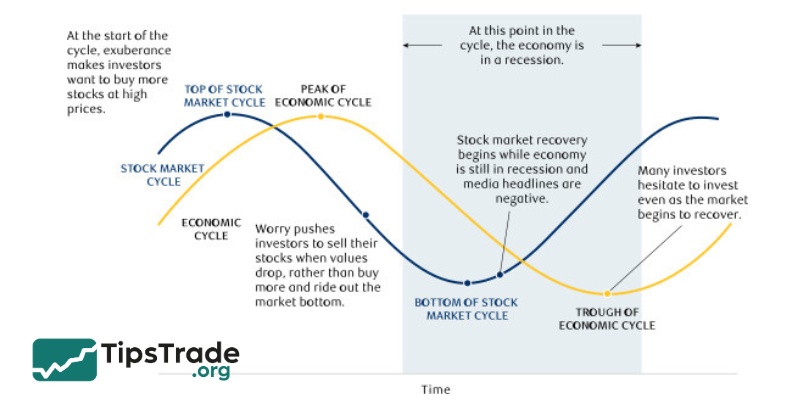
How macroeconomic factors impact the stock markets
Macroeconomic factors have a significant impact on all sectors and industries in the economy, including the stock market. Let’s walk through a few key macroeconomic factors that affect the stock markets.
Interest rates
Changes in interest rates can have a significant impact on the stock market. When interest rates are low, it is easier for businesses to borrow money, which in turn stimulates investment and economic growth. This generally has a positive impact on the stock market. Conversely, when interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing becomes higher, leading to reduced investment and slower growth, which has a negative impact on the stock market.

Inflation
Inflation refers to the rate at which prices of goods and services increase over time. Inflation can have a significant impact on the stock market. When inflation is high, consumer purchasing power decreases and investment tends to stagnate, negatively affecting the stock market. Conversely, when inflation is low, consumer spending and investment tend to increase, positively affecting the stock market.

Gross domestic product (GDP)
GDP is a measure of a country’s economic output. When GDP is high, it indicates a strong economy and often has a positive impact on the stock market. Conversely, when GDP is low, it reflects a weak economy and can have a negative impact on the stock market.

Policy
Fiscal policy and monetary policy direct the flow of money in the economy. A decrease in interest rates corresponds to a loose monetary policy regime. Similarly, an increase in government spending indicates a loose fiscal policy regime. Loose policies generally lead to an increase in liquidity and money supply in the market.
Note: Too much money in the economy creates asset bubbles and results in eventual stock market crashes.

Global events
Global events such as wars or natural disasters can have a major impact on the stock market. These events often increase volatility and uncertainty, causing stock prices to fluctuate widely.

Tips for stock investors
With the constant volatility of stock prices in the context of the macroeconomy, many investors have had to give up. Here are a few tips for investors on how to cope with them:
- Research and analyze macroeconomic indicators carefully: This helps investors make informed decisions based on an understanding of inflation, interest rates, economic growth, foreign exchange rates and other economic factors.
- Diversify invests: Diversifying investments across different stocks and sectors helps to reduce the risk of macroeconomic conditions affecting a particular sector.
- Learn more about investment companies: This ensures that investors understand the long-term growth potential of companies and are not overly affected by the macroeconomic situation.
- Make decisions based on available data and information: Always rely on reliable data and information to make investment decisions rather than on emotions or rumors.
- Only invest what you can afford to lose: To avoid taking too much financial risk, invest an amount that you can afford to lose, not more than you can afford to lose.
- Investment conversion: If you find that the macroeconomic situation is not favorable for the stocks you are investing in, consider switching to investing in companies that have the potential to increase product or service prices to protect your investment.

Conclusion
In summary, when studying the impact of macroeconomic factors on the stock market, investors need to consider them within a comprehensive picture that includes other macroeconomic factors to gain a holistic perspective. In addition, investors also need to consider indicators of the company’s financial capacity and growth potential to choose the appropriate investment timing and portfolio.
See more:

