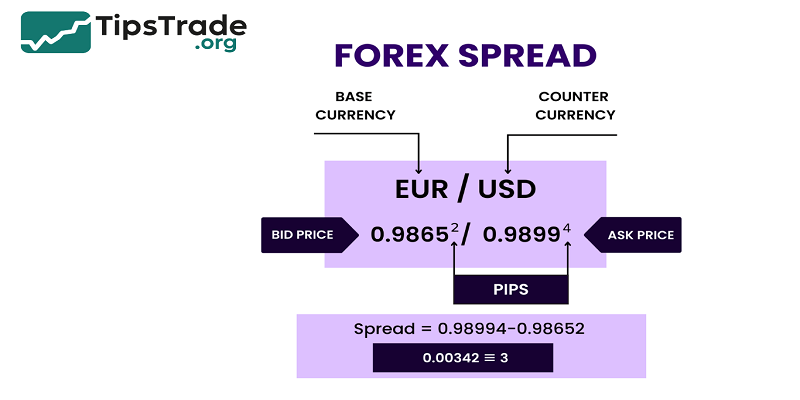
Forex Spread Matters? When new traders step into the forex market, one of the first concepts they encounter is the spread. Simply put, the forex spread is the difference between the bid price (the price you can sell a currency pair) and the ask price (the price you can buy it).
What Is Forex spread?

- At its core, a forex spread is the cost of trading, built into the price quote of every currency pair. If EUR/USD is quoted as 1.1000 / 1.1002, the spread is 2 pips.
- That means the broker charges you 2 pips to enter this trade.
- Spreads exist because brokers or liquidity providers facilitate transactions between buyers and sellers.
- Instead of charging a fixed fee upfront, most brokers embed their fee into this bid-ask difference.
- For beginners, recognizing the spread as a hidden cost is crucial—it may not seem obvious at first glance, but it shapes long-term profitability.
- Bid = Sell price (what buyers are willing to pay)
- Ask = Buy price (what sellers are asking)
- Spread = Ask − Bid
This structure is universal across financial markets—stocks, commodities, and cryptocurrencies—but forex spreads are typically smaller due to the high liquidity of currency trading.
>See more:
- What is Pip in Forex? Accurate calculation guide for traders
- Top 10 best forex currency pairs to trade in 2025
- What are exchange rates? How to read and analyze rates in Forex
Bid vs. Ask: The Foundation of Spreads

The bid price reflects the maximum price a buyer is ready to pay for a currency pair. The ask price reflects the minimum price a seller is willing to accept.
For example:
- EUR/USD = 1.1000 (Bid) / 1.1002 (Ask)
- If you buy, you pay 1.1002.
- If you sell immediately, you receive 1.1000.
- That 2-pip difference is your trading cost.
Spreads ensure there is always a middle ground between supply and demand. In forex, where daily trading volume exceeds $7.5 trillion (Bank for International Settlements, 2022), spreads can be extremely tight—sometimes as low as 0.1 pips during liquid hours.
How Are Spreads Measured? Pips and Points
Spreads are usually measured in pips (percentage in points). A pip is the fourth decimal place of most currency quotes. For example:
- EUR/USD: 1.1000 → 1 pip = 0.0001
- USD/JPY: 145.00 → 1 pip = 0.01
If the bid is 1.1000 and the ask is 1.1003, the spread is 3 pips. Some brokers also display spreads in points, where 1 pip = 10 points.
Understanding pip value helps traders measure costs in dollar terms.
For instance, on a standard lot (100,000 units), 1 pip = $10 for EUR/USD. That means a 2-pip spread equals a $20 cost per trade.
Fixed vs. Variable (Floating) Spreads
Forex brokers typically offer two main spread models:
- Fixed Spreads:
- Remain constant regardless of market conditions.
- Often provided by market maker brokers.
- Advantage: predictable costs.
- Disadvantage: usually wider than variable spreads.
- Variable (Floating) Spreads:
- Change based on market liquidity and volatility.
- Often tighter during high-volume trading sessions.
- Advantage: lower costs in normal conditions.
- Disadvantage: can widen dramatically during news events.
Beginners may prefer fixed spreads for stability, while experienced traders often choose variable spreads to benefit from tighter conditions.
How to Calculate Forex Spread
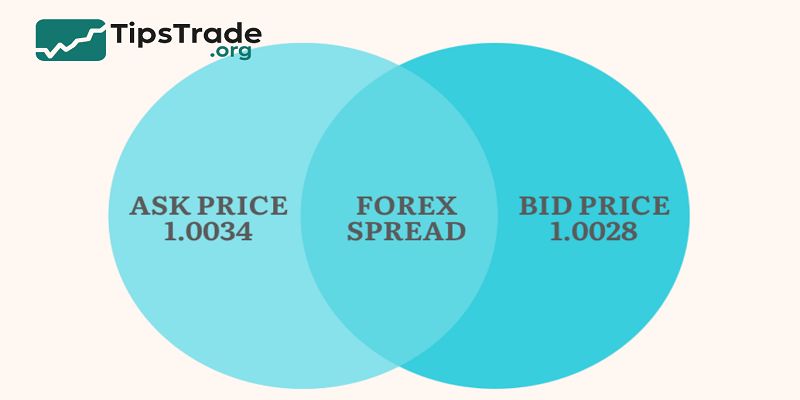
The formula is straightforward:
Spread = Ask Price − Bid Price
Example:
- GBP/USD quote: 1.2500 / 1.2502
- Spread = 1.2502 − 1.2500 = 0.0002 (2 pips)
To convert the spread into trading cost:
- On a standard lot (100,000 units): 2 pips = $20
- On a mini lot (10,000 units): 2 pips = $2
- On a micro lot (1,000 units): 2 pips = $0.20
This calculation shows why scalpers—who trade frequently—must pay close attention to spreads, as costs add up quickly.
Real Examples of Forex spread
Let’s look at spreads for popular pairs under normal market conditions:
| Currency Pair | Typical Spread (Raw ECN) | Typical Spread (Standard) |
| EUR/USD | 0.1 – 0.3 pips | 1.0 – 1.5 pips |
| GBP/USD | 0.2 – 0.5 pips | 1.2 – 1.8 pips |
| USD/JPY | 0.1 – 0.4 pips | 1.0 – 1.5 pips |
| AUD/USD | 0.2 – 0.6 pips | 1.0 – 1.6 pips |
(Source: broker data 2023–2024 from IC Markets, Exness, Oanda)
Notice how raw spread accounts often advertise near-zero spreads, but they charge commissions separately. Standard accounts bundle the fee into a wider spread.
Factors That Influence Forex Spreads
Liquidity
- Highly traded pairs (EUR/USD, USD/JPY) have the tightest spreads because of deep liquidity.
- Exotic pairs (USD/TRY, USD/ZAR) often have spreads above 10 pips due to limited trading volume.
Volatility and News Events
- During high-impact events (e.g., Nonfarm Payrolls, central bank announcements), spreads can widen dramatically—sometimes by 10x or more. Traders often avoid entering positions right before such events.
Trading Sessions
- Spreads are tighter during overlapping sessions (London + New York) and wider during low-liquidity hours (Asian midnight).
Broker Type and Account Model
- ECN/Razor accounts: very tight spreads + commission.
- Market makers: wider spreads but no commission.
- Understanding these factors helps traders choose when and where to trade to minimize costs.
How Spreads Affect Trading Performance

Spreads directly influence profitability. Let’s break it down:
- Entry/Exit Costs: Every trade starts with a small loss equal to the spread. You must overcome this cost before reaching break-even.
- Scalping: Spread is critical because profits per trade are small. Even 1–2 pips can make or break a strategy.
- Day/Swing Trading: Spreads matter less but still accumulate over time.
- Slippage + Commission + Spread: Real trading cost includes all three.
Example: If you scalp EUR/USD 20 times a day with a 1.2-pip spread, that equals 24 pips in daily cost—roughly $240 per standard lot.
Types of Spread and Broker Pricing Models
Raw Spread + Commission
- Near-zero spreads advertised (e.g., 0.0–0.2 pips).
- $6–$7 commission per round lot.
- Favored by professional traders.
All-Inclusive Spread (No Commission)
- Wider spreads (1.0–1.5 pips).
- Commission built into the spread.
- Simpler for beginners.
Fixed Spread
- Spread does not change, even during news.
- Usually higher (2–3 pips).
Special Products (CFDs, Exotic pairs)
- May carry much higher spreads due to risk and liquidity issues.
Comparing Spreads Between Forex Brokers
Spreads vary significantly among brokers. Below is a simplified comparison:
| Broker | EUR/USD (Raw) | EUR/USD (Standard) | Commission |
| IC Markets | 0.1 pips | 1.0 pips | $7 / lot |
| Exness | 0.0 pips | 1.2 pips | $6 / lot |
| XM | 0.2 pips | 1.6 pips | $7 / lot |
| Oanda | 0.2 pips | 1.2 pips | None |
Traders should compare both spread + commission to calculate total cost, not just advertised “zero spread.”
How to Reduce Trading Costs Caused by Spreads
Practical strategies to minimize spread-related costs:
- Trade during high-liquidity sessions (London, New York overlap).
- Focus on major pairs (EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY).
- Choose brokers with low spreads + transparent fees.
- Use limit orders to avoid spread slippage.
- Avoid entering trades during major economic news.
These habits can cut trading costs by 30–50% over the long run.
Common Misconceptions About Forex Spreads
- “Zero Spread = Free Trading” → False.
- Zero spread accounts still charge commission.
- “Spread is the only cost” → False.
- Commission and overnight swap fees also matter.
- “Fixed spreads never change” → Misleading.
- Even fixed spreads may widen under extreme volatility.
- “My broker hides spreads” → Sometimes True.
- Some market makers widen spreads during illiquid conditions. Always check broker transparency.
Conclude
Forex spread is a fundamental concept every trader must understand to navigate the currency market effectively. Forex spread refers to the difference between the bid (selling) price and the ask (buying) price of a currency pair, representing the primary cost of trading. Knowing how forex spread works helps traders to manage transaction costs, choose the right broker, and optimize their trading strategy.