Forex legal is a critical topic that every trader must understand to ensure safe and compliant participation in the currency markets. Forex legal matters cover regulations, licensing of brokers, and trader protections that vary by country and region. Through this article, let’s explore in detail with tipstrade.org the essential legal frameworks and best practices every forex trader should be aware of to avoid legal pitfalls and trade confidently.
Is Forex Trading Legal? (Global Overview)
Forex Legal in Most Countries
Forex trading is legal in the majority of countries, especially those with advanced financial systems. Governments regulate the market to protect investors and ensure fair practices. For example:
- United States: Overseen by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the National Futures Association (NFA). These agencies enforce strict rules on leverage, transparency, and broker conduct.
- United Kingdom: The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) requires brokers to maintain capital reserves and protect client funds in segregated accounts.
- Australia: The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) ensures brokers operate under strict disclosure rules.
- European Union: CySEC (Cyprus), BaFin (Germany), and other national regulators enforce EU-wide protections under MiFID II.
- Japan: The Financial Services Agency (FSA) regulates leverage and requires brokers to protect traders against excessive risk.
- Singapore: The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) monitors all Forex activities.
Countries with Restrictions or Bans
While Forex is legal in most parts of the world, some countries impose restrictions or outright bans.
- India: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) allows only limited currency pairs and requires trading via authorized exchanges. Retail Forex trading with offshore brokers is prohibited.
- China: Strict capital controls and foreign exchange regulations mean retail Forex is largely restricted. Traders often access offshore brokers, which poses legal risks.
- South Korea: Heavily regulated with strict rules on leverage and money transfers abroad.
- Nigeria and some African countries: Authorities issue frequent warnings about unregulated Forex schemes and Ponzi scams.
The main reasons for restrictions are:
- Preventing money laundering.
- Protecting citizens from high-risk leveraged products.
- Preserving capital stability and preventing currency manipulation.
>>See more:
- What is Forex? The Complete Guide for Beginners
- What are exchange rates? How to read and analyze rates in Forex
- Top 10 best forex currency pairs to trade in 2025
- Essential Forex Orders every trader must know
- What is forex trading? A detailed guide to forex trading from A – Z
Key Regulations Governing Forex Legal Trading

Licensing and Regulatory Authorities
A broker’s license is the first sign of legality. Licensed brokers must comply with strict rules set by their regulators. Examples include:
- United States: RFED (Retail Foreign Exchange Dealer) and FCM (Futures Commission Merchant) registration under the CFTC. Verification available at nfa.futures.org.
- United Kingdom: FCA license ensures client funds are segregated and covered by compensation schemes.
- Australia: ASIC requires brokers to meet high capital adequacy standards.
- Cyprus (EU): CySEC regulates most EU-based brokers, especially those serving international clients.
- Singapore: MAS licenses brokers and monitors cross-border transactions.
Capital Requirements, Transparency, and Risk Disclosure
Regulated brokers must demonstrate financial stability by maintaining minimum capital requirements. This prevents insolvency and ensures client withdrawals are protected. They also must:
- Publish risk disclosure statements to warn clients of potential losses.
- Provide transparent pricing and spreads.
- Submit regular financial reports to regulators.
- Offer access to dispute resolution mechanisms if conflicts arise.
Such transparency builds trust and helps traders avoid dishonest brokers that promise unrealistic profits.
Leverage and Margin Restrictions
One of the most important aspects of Forex regulation is leverage control. High leverage increases profit potential but also magnifies risk.
- U.S. regulators (CFTC/NFA) limit leverage to 50:1 for major pairs and 20:1 for minors.
- European Union (ESMA rules) caps leverage at 30:1 for majors.
- Japan restricts leverage to 25:1.
- Australia (ASIC) limits leverage to 30:1 for retail traders.
These measures protect beginners from excessive losses. Unregulated brokers often advertise leverage as high as 1,000:1, which is a red flag for risky practices.
Penalties and Enforcement
Regulators actively monitor brokers. Penalties for violations include:
- Hefty fines (in the millions of dollars).
- Revocation of licenses.
- Legal prosecution for fraud or market manipulation.
- Public warnings posted on regulator websites.
Example: In 2017, FXCM, a major broker, was fined $7 million by the CFTC for misleading clients and subsequently banned from operating in the U.S. This demonstrates how enforcement protects traders and preserves market integrity.
Forex in Vietnam and Southeast Asia
Legal Framework in Vietnam
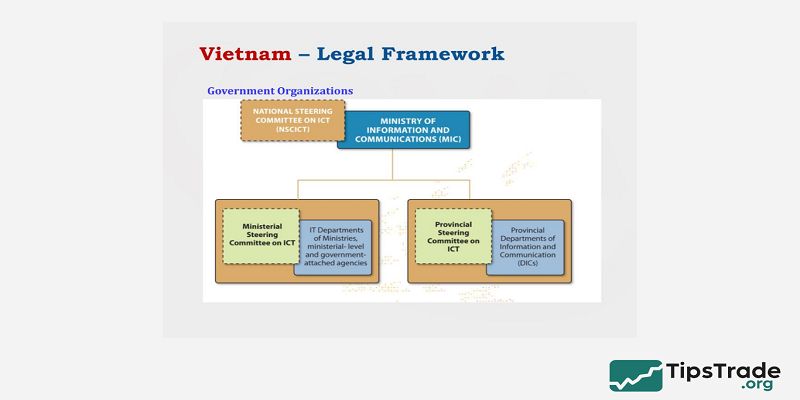
Vietnam does not currently have a clear regulatory framework for retail Forex trading. The State Bank of Vietnam has not issued licenses for international brokers to operate domestically. This means:
- Vietnamese individuals trading Forex with offshore brokers are operating in a legal “grey zone.”
- There is no domestic legal protection if disputes arise with foreign brokers.
- Advertising unlicensed Forex trading services within Vietnam may be considered illegal.
As a result, many Vietnamese traders rely on international brokers regulated abroad (e.g., FCA, ASIC, CySEC). However, this comes with risks since local courts may not recognize disputes.
Risks for Vietnamese Traders Using Offshore Brokers

Some of the key risks include:
- Scams: Many fraudulent brokers target Vietnamese traders through social media promises of “guaranteed returns.”
- Blocked accounts: Offshore brokers can freeze accounts without warning, leaving traders with little legal recourse.
- Money transfer issues: Sending or withdrawing funds internationally may trigger scrutiny from local banks.
- Taxation: Profits from Forex trading may be subject to income tax, but reporting remains unclear under Vietnamese law.
Therefore, Vietnamese traders must exercise extreme caution and choose only well-regulated brokers with a proven history of transparency.
How to Identify a Legal and Reliable Forex Broker
Verify License and Registration
The most reliable way to check broker legality is by verifying its license number with a regulator. Steps include:
- Visit the official regulator’s website (e.g., nfa.futures.org for the U.S., register.fca.org.uk for the UK).
- Search the broker’s company name or license number.
- Confirm details match the broker’s official website (address, registration number, legal entity).
Transparent Costs: Spreads and Commissions

A regulated broker provides clear details on:
- Spreads (difference between buy and sell price).
- Commission fees.
- Overnight swap rates.
Hidden fees are a warning sign of unreliable brokers. Always compare costs between licensed providers to ensure fairness.
Platform Reliability and Leverage
Reputable brokers use trusted platforms such as MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), or proprietary platforms with strong security measures. Features to look for:
- Reasonable leverage levels aligned with regulatory caps.
- Real-time execution with minimal slippage.
- Secure two-factor authentication for account safety.
User Reviews and Disciplinary History
Traders should also review:
- Independent broker reviews on financial websites.
- User experiences on forums and social media.
- Disciplinary actions or warnings listed by regulators.
Risk Management and Client Protection
Licensed brokers must offer risk management features, such as:
- Negative balance protection.
- Stop-loss orders.
- Segregated client funds.
Legal Risks and Real Case Studies

Common Forex Scams
Unregulated Forex brokers and Ponzi schemes often lure beginners with:
- Promises of “guaranteed profits”.
- Excessive leverage offers (500:1 or more).
- Lack of official licensing information.
- Pyramid recruitment models.
Example: In 2020, authorities in India shut down several fraudulent Forex investment schemes that collected millions from unsuspecting investors.
Major Enforcement Cases
- FXCM (U.S., 2017): Fined and banned for misrepresenting conflicts of interest.
- IronFX (Cyprus, 2015): Faced multiple lawsuits for withdrawal restrictions.
- Multiple brokers in Nigeria (2019–2022): Shut down for running Ponzi schemes disguised as Forex investments.
These cases show why traders must stick to brokers under credible regulators.
Legal Protection for Traders
When trading with a licensed broker, clients benefit from:
- Compensation schemes (e.g., UK’s Financial Services Compensation Scheme covers up to £85,000 per client).
- Access to regulatory dispute resolution services.
- Transparency in court cases if fraud occurs.
Safe and Legal Participation in Forex
Step 1: Choose a Licensed Broker
- Always start with brokers registered under top-tier regulators such as the FCA, ASIC, CFTC/NFA, MAS, or FSA Japan.
Step 2: Open a Demo Account
- Test the broker’s trading conditions using a demo account. Check spreads, execution, and platform stability.
Step 3: Trade Small and Manage Risk
- Begin with small deposits.
- Use leverage conservatively (no more than 10:1 as a beginner).
- Apply stop-loss orders.
Step 4: Stay Updated on Regulations
- Forex laws change over time. Subscribe to regulator newsletters or financial news outlets to stay informed.
Word Count
Forex legal is a crucial aspect that ensures trading activities comply with laws and regulations to protect traders and maintain market integrity. Understanding forex legal frameworks helps investors avoid scams, choose regulated brokers, and trade with confidence. In conclusion, forex legal compliance is fundamental for creating a safe and transparent trading environment, which supports long-term success in the forex market.

