Forex currency pairs are the foundation of every trade in the dynamic foreign exchange market, representing the exchange rates between two different national currencies. Understanding forex currency pairs is essential for traders who want to navigate the market with confidence, manage volatility, and capitalize on market movements.
What Are Forex Currency Pairs?
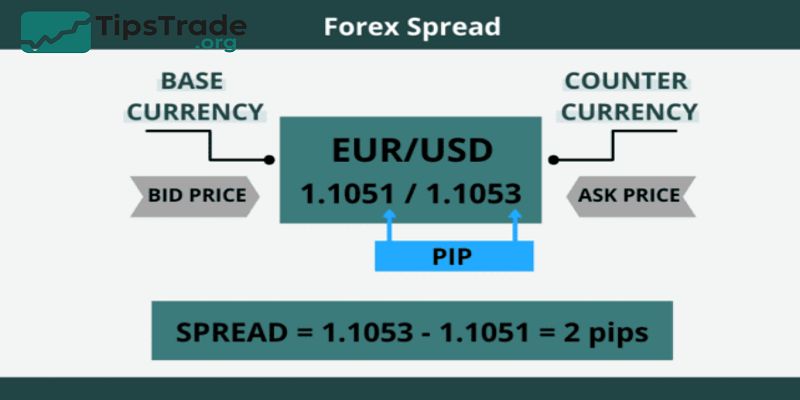
Currencies are always quoted in pairs because you’re simultaneously buying one currency and selling another.
- Base currency: The first currency in the pair (e.g., EUR in EUR/USD).
- Quote currency: The second currency in the pair (e.g., USD in EUR/USD).
Example:
If EUR/USD = 1.1200, it means 1 EUR = 1.12 USD.
Forex quotes also include Bid and Ask prices:
- Bid: the price at which traders sell the base currency.
- Ask: the price at which traders buy the base currency.
The difference is called the spread, which represents a transaction cost.
>See more:
- What is Pip in Forex? Accurate calculation guide for traders
- Top 10 best forex currency pairs to trade in 2025
- What are exchange rates? How to read and analyze rates in Forex
Types of Forex Currency Pairs
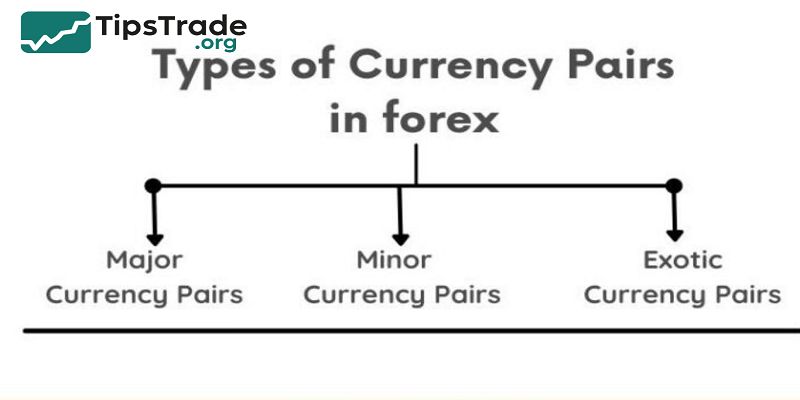
Major Currency Pairs
Majors always include the USD and another highly traded currency. They are the most liquid, with the tightest spreads.
List of Major Pairs:
- EUR/USD
- GBP/USD
- USD/JPY
- USD/CHF
- USD/CAD
- AUD/USD
- NZD/USD
Why trade majors?
- Highest liquidity
- Lower transaction costs
- Widely covered in financial news
Minor Currency Pairs (Crosses)
Minors don’t include the USD but involve other major currencies.
Examples:
- EUR/GBP
- GBP/JPY
- AUD/JPY
Minors often show higher volatility, providing trading opportunities but with slightly higher spreads than majors.
Exotic Currency Pairs
Exotics combine a major currency with an emerging market currency.
Examples:
- USD/TRY (Turkish Lira)
- USD/SEK (Swedish Krona)
- EUR/ZAR (South African Rand)
Risks of Exotics:
- Low liquidity
- Higher spreads
- Sudden unpredictable movements
Table: Types of Forex Currency Pairs
| Type | Example Pairs | Liquidity | Spread | Risk Level |
| Majors | EUR/USD, USD/JPY | High | Low | Low |
| Minors | EUR/GBP, GBP/JPY | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Exotics | USD/TRY, EUR/ZAR | Low | High | High |
How to Read Forex Currency Pairs
Example: EUR/USD = 1.1200
- If the rate increases to 1.1250 → EUR strengthens, USD weakens.
- If the rate drops to 1.1100 → EUR weakens, USD strengthens.
Key Concepts:
- Pip (percentage in point): The smallest price change (0.0001 for most pairs).
- Profit/Loss: A movement of 10 pips in a standard lot (100,000 units) of EUR/USD equals $100.
- Spread: The cost of trading; tighter spreads reduce transaction expenses.
Factors That Influence Currency Pairs
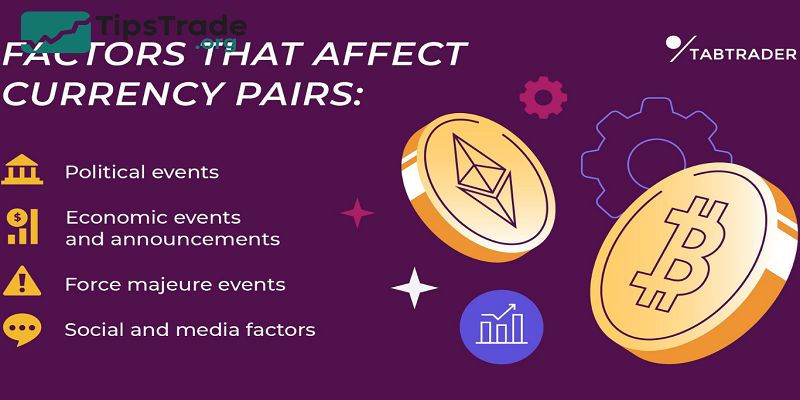
Economic Indicators
- Interest rates: Higher rates attract investors, strengthening a currency.
- GDP growth: Indicates economic strength.
- Inflation data: Affects central bank policies.
Example: The U.S. Federal Reserve raising rates often boosts USD pairs.
Political & Geopolitical Events
- Elections, wars, or policy changes can create volatility.
- Example: Brexit had a major impact on GBP/USD and EUR/GBP.
Market Sentiment & News
- Global news drives short-term moves.
- Safe-haven currencies (USD, JPY, CHF) often rise during crises.
Most Popular Forex Currency Pairs for Beginners
EUR/USD
- Most traded pair worldwide
- Lowest spreads, high liquidity
- Recommended for beginners
GBP/USD (“Cable”)
- More volatile than EUR/USD
- Influenced by U.K.–U.S. relations
USD/JPY
- Sensitive to global risk sentiment
- Popular among both beginners and professionals
AUD/USD & NZD/USD
- Correlated with commodities like gold and agriculture
- Useful for traders following global commodity trends
USD/CHF
- Considered a safe-haven pair
- Often stable during financial uncertainty
Pros and Cons of Trading Different Types of Pairs
- Majors: Pros – liquidity, tight spreads. Cons – lower volatility.
- Minors: Pros – good volatility. Cons – higher spreads.
- Exotics: Pros – unique opportunities. Cons – high costs, unpredictable.
How to Choose the Right Forex Currency Pairs
- Match pairs to trading style:
- Scalpers → Majors (tight spreads).
- Swing traders → Minors (larger price swings).
- Volatility preference: Beginners should start with stable majors.
- Time zone: JPY and AUD pairs move more in the Asian session.
- Correlations: Example – EUR/USD and USD/CHF often move in opposite directions.
Tips for Trading Forex Currency Pairs as a Beginner

- Start with 1–2 major pairs to reduce complexity.
- Use a demo account before going live.
- Follow an economic calendar to anticipate key news.
- Always apply risk management (stop-loss, position sizing).
Common Mistakes Traders Make with Currency Pairs
- Trading too many pairs at once.
- Ignoring spreads and liquidity.
- Overtrading exotic pairs.
- Failing to understand correlations (e.g., EUR/USD vs. USD/CHF).
Advanced Insights into Forex Currency Pairs
Currency Correlations
- Positive correlation: EUR/USD and GBP/USD.
- Negative correlation: EUR/USD and USD/CHF.
Understanding correlations avoids double exposure.
Safe-Haven vs. Risk-On Currencies
- Safe-haven: USD, JPY, CHF (perform well in crises).
- Risk-on: AUD, NZD, emerging currencies (perform well during global growth).
Impact of Global Markets (Commodities & Indices)
- Oil prices heavily influence USD/CAD.
- Gold often correlates with AUD/USD.
Conclude
Forex currency pairs are the cornerstone of the foreign exchange market and essential to every trader’s success. Forex currency pairs represent the value of one currency relative to another, providing opportunities to profit in both rising and falling markets. Understanding the dynamics of forex currency pairs, including major, minor, and exotic categories, helps traders make informed decisions and manage risks effectively.