Compare CFDs and Stocks is a common topic for traders and investors who are deciding which financial instrument best suits their goals, risk tolerance, and trading style. While both CFDs and stocks offer opportunities to profit from market movements, they differ significantly in terms of ownership, leverage, costs, and trading flexibility. In this article, we will explore the key differences and similarities between CFDs and stocks to help you make a more informed trading decision. Let’s get started!
What are CFDs?
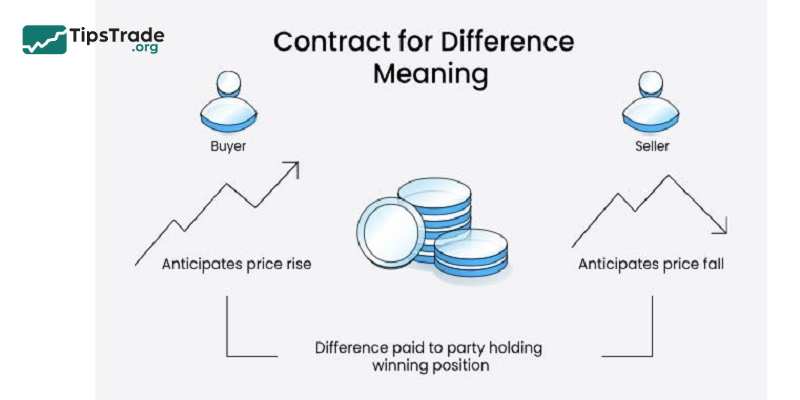
CFD derivatives trading, short for Contracts for Difference, allows traders to speculate on price movements both (upward and downward) of fast-moving global financial assets such as commodities, stocks, forex, and precious metals. Specifically, when a contract is closed, the trader and the broker exchange the difference between the asset’s opening price and closing price. You can make a profit or incur a loss depending on the direction in which the chosen asset moves.
>>Learn more about CFD trading and how it works.
What are Stocks?
A stock represents a collection of shares that signify partial ownership in a publicly listed company. By purchasing a stock, traders own a small portion of that corporation. This is because they pay the market value of the stock and earn profits or incur losses based on its price movements.

Compare CFDs and Stocks: Key similarities
Compare CFDs and Stocks, both of them have their own similarities and it is important to recognise both their similarities and differences. Below are 3 similarities between CFDs and stocks trading:
Both allow traders to take advantage of price movements
For Contract for Difference (CFD), it allows traders the opportunity to take advantage of the falling and rising prices of underlying financial assets. A stock also allows both traders and investors to take advantage of the price movement of the shares.

Access to global markets
Both CFDs and stocks provide traders access to a wide range of global markets. Traders can trade various global companies listed on various stock exchanges around the world such as the famous The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), London Stock Exchange, Tokyo Stock Exchange, and many others.
These stock exchanges represent companies from different industries and sectors, allowing traders to diversify their portfolios across the globe.

Accessible through online platforms
CFDs and stocks can both be traded on online trading platforms and mobile apps. These platforms offer traders real-time price data, charting tools and order execution capabilities making it convenient for traders to participate in the financial markets.
Compare CFDs and Stocks: Key differences
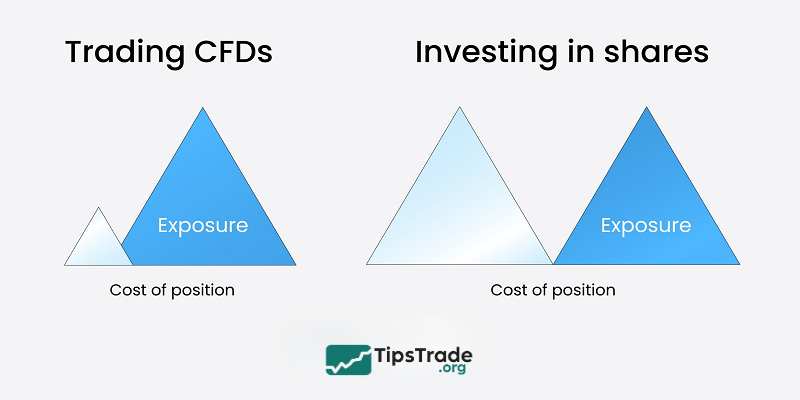
Leverage and margin requirements
CFD Trading:
- Uses leverage to amplify market exposure
- Requires only a percentage of the position value as margin
- Higher potential returns or losses due to leverage
Stock Trading:
- Requires full capital for purchase
- No leverage applied to available cash
- Lower risk but requires more capital
- Direct correlation between investment and potential returns
Asset variety and market access
CFD platform offerings:
- 2,500+ instruments across multiple asset classes
- Forex pairs (EUR/USD, GBP/USD)
- Commodities (Gold, Oil, Agricultural products)
- Indices (FTSE 100, S&P 500)
- Cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin, Ethereum)
- ETFs and Options
Invest platform offerings:
- 1,200+ individual stocks from global exchanges
- 90+ ETFs for diversified exposure
- Access to new IPOs when companies go public
- Focus on blue-chip and growth stocks

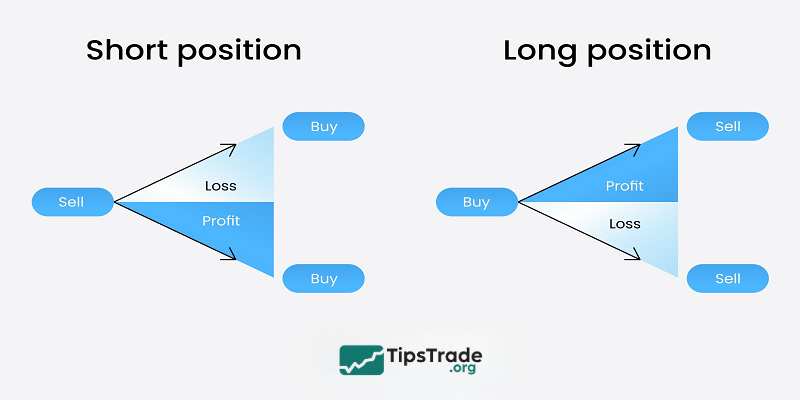
Short selling capabilities
CFD Trading:
- Sell positions without prior ownership
- Take advantage of falling markets
- Essential for hedging strategies
- No borrowing costs for short positions
Stock Trading:
- Traditional buy-first approach
- Limited short-selling options
- Requires stock borrowing arrangements
- Higher costs for short positions
Asset ownership and rights
CFD Trading:
- No physical asset ownership
- No voting rights or shareholder benefits
- No dividend payments (dividend adjustments may apply)
- Pure price speculation focus
Stock Trading:
- Full legal ownership of shares
- Voting rights in company decisions
- Dividend payments where applicable
- Long-term capital appreciation potential
Costs and fees structure
CFD Trading Costs:
- Overnight financing fees for positions held after market close
- Spread-based pricing
- No commission on most instruments
- Other fees may apply
Stock Trading Costs:
- No overnight fees for long positions
- Potential custody fees
- Lower ongoing costs for buy-and-hold strategies
CFD vs Stock trading: Which one suits you?
Both come with their own advantages and disadvantages. So, choosing between the two depends on your trading style, expectations, and capital available for investments.
Choose CFD Trading If:
- You prefer short-term trading opportunities
- Want exposure to multiple asset classes
- Seek to take advantage of both rising and falling markets
- Have an x amount of capital but want larger market exposure
- Interested in earnings season speculation

Choose Stock Trading If:
- Building long-term investment portfolios
- Seeking dividend income
- Want actual ownership of company shares
- Prefer lower-risk investment approaches
- Planning for retirement or long-term financial goals
Final thoughts
In summary, when you compare CFDs and Stocks, it becomes clear that each instrument has its own unique advantages and disadvantages tailored to different trading styles. If you prioritize security, ownership rights, and long-term dividends, stocks remain the optimal choice. On the other hand, if you are an active trader looking to utilize leverage and profit from both rising and falling markets, CFDs could be your go-to tool. Carefully consider your financial goals and risk tolerance to make the smartest investment decision for your portfolio.

