To become a wise Forex trader, you need to clearly understand the impact between central bank vs forex. Central banks act as the “conductors” guiding global money flows, while the forex market is where those changes are reflected most quickly. In the article below, Tipstrade.org will clarify the impact of central bank vs forex, providing you with a basis for building safer and more effective trading strategies.
What is a central bank?
A central bank is an agency responsible for regulating commercial banks, setting central bank interest rates, and maintaining a country’s financial stability.
Central banks intervene in financial markets through:
- Open Market Operations: Open market operations (OMO) are the process by which governments buy and sell government securities (bonds) on the open market, with the aim of increasing or decreasing the amount of money in the banking system.
- Federal Reserve Rate: The federal funds rate, also known as the discount rate or federal funds rate, is set by the monetary policy committee to increase or decrease economic activity. This may seem counterintuitive, but an overheated economy leads to inflation, and this is the tool central banks use to keep inflation in check.
Central banks also act as lenders of last resort. If a government has a low debt-to-GDP ratio and cannot raise money through bond auctions, the central bank can lend money to the government to meet temporary liquidity shortages.
Having the central bank as the lender of last resort also increases investor confidence. Investors feel more confident that governments can meet their debt obligations, and this helps reduce governments’ borrowing costs.

>>Read more:
- What is Forex? The Complete Guide for Beginners
- Interest rate forex impact: How it affects currency value
- Important Economic Indexes Every Trader Needs To Know
- What are exchange rates? How to read and analyze rates in Forex
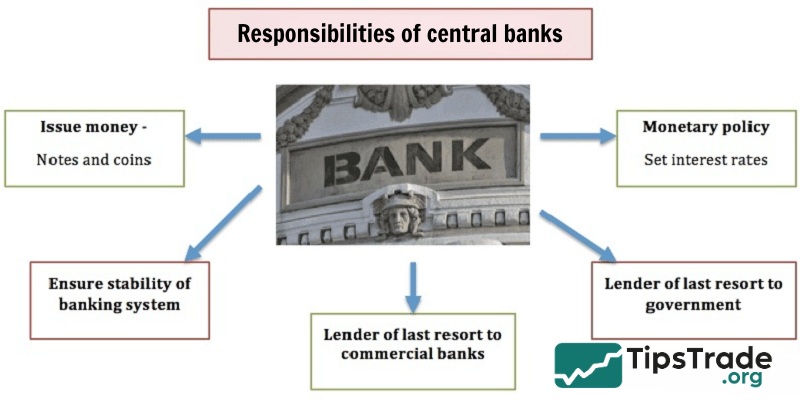
Responsibilities of central banks
Central Banks are established to carry out tasks that serve the public interest. These responsibilities may vary from country to country, but the main responsibilities include:
- Achieving and maintaining price stability: Central Banks are tasked with protecting the value of their currencies. This is done by maintaining a moderate level of inflation in the economy.
- Promote the stability of the financial system: Central Banks force Commercial Banks to undergo a series of stress tests. This helps reduce risks in the financial sector.
- Promoting balance and sustainable development:Generally, there are two main ways a country can stimulate its economy. These are through Fiscal Policy (Government spending); Monetary Policy (Central Bank intervention). When governments run out of money, Central Banks can initiate monetary policy to stimulate the economy.
- Supervision and regulation of financial institutions:Central Banks are tasked with regulating and supervising Commercial Banks, for the common good.
- Reduce unemployment: In addition to price stability and sustainable growth, central banks are responsible for reducing unemployment. This is one of the goals of the Federal Reserve.
Most powerful central banks in the world
Below is a list of the most powerful central banks in the world today:
U.S. Federal Reserve System (Fed)
The FED is the place that issues and controls the money supply. The US Federal Reserve is responsible for and regulates the USD. This is considered the most widely traded currency in the world (according to the 2016 Triennial Central Bank survey).
The actions of the Fed affect not only the US dollar but also other currencies. That is why the actions of the US Federal Reserve receive so much attention. The Fed aims to keep prices stable, maximize employment and maintain moderate long-term interest rates.

European Central Bank (ECB)
Unlike the Central Banks of countries, the European Central Bank ECB acts as the central bank for all members of the European Union. ECB stands for European Central Bank. The European Central Bank is located in Frankfurt, Germany. It was established in 1998 by the Treaty of Amsterdam.
It controls monetary policy for the entire eurozone. The member countries of the zone include Australia, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia and Spain.

The role of the ECB
The European Central Bank is supervised by a Governing Council consisting of six Executive Board members, one of whom serves as President. Executive Board members are appointed by the European Council.
The main mission and functions of the European Central Bank (ECB) are to maintain price stability and financial stability.
- To keep prices stable, the European Central Bank (ECB) influences short-term interest rates in the eurozone. (target rate ≈ 2%)
- In times of crisis, the ECB can maintain financial stability by adding liquidity to the system by buying bonds in the open market OMO or by cutting interest rates to extremely low levels to help debtors pay their debt obligations.
If the European Central Bank does not add liquidity during the crisis, the entire financial system could collapse.
Note: Rising inflation does not mean the European Central Bank will raise interest rates.
Impact of ECB interest rates
Interest rates are set by the European Central Bank. As the Central Bank of the European Union, changes to ECB interest rates have an impact on the Euro and the economy as a whole.
- The euro tends to rise and fall based on changes in expected interest rates, not just actual interest rates. Historically, quantitative easing (QE) has had a similar effect on the euro as interest rates, and has only been used in times of crisis.
- The European Central Bank (ECB) lowers interest rates as they try to stimulate the economy (GDP) and vice versa.
Bank of England (BOE)
The Bank of England (BOE) is the central bank of England. Their mission is to promote and maintain monetary and financial stability. Founded in 1694, Bank of England BOE is a bank owned by the British Government. However, when it comes to setting monetary policy, it is an independent body.

BOE’s Duties
The BOE’s roles include setting monetary policy – which includes setting interest rates and using other tools to stimulate or contract the economy; issuing UK banknotes; supervising some banking payment systems; and ensuring the stability and safety of the financial system.
Bank of England BOE is responsible for:
- Monetary Stability – Keeping Prices and Inflation Stable
- Financial stability – Is the stability and growth of the economy
From a forex trader’s perspective, currency stability is the main factor influencing the GBP spot exchange rate.
The Bank of England’s impact on the market
This is the body that sets monetary policies to boost or slow down the UK economy, so the BOE’s decisions have impacts on the Pound and the UK economy.
Here are the general principles of how interest rates affect the pound and the stock market, although they have different impacts:
|
Adjust interest rate |
Impact on the Pound | Impact on stocks |
| Higher expected interest rates | Power Up
Pound Sterling |
Negative |
| Lower expected interest rates | Reduced power
Pound Sterling |
Positive |
The Bank of England BOE lowered interest rates when they were trying to stimulate the economy. Raise interest rates when they are trying to curb inflation caused by the economy growing above its potential (overheating).
Let’s take a look at the GBP/USD pair below. On August 4, 2016, the Bank of England cut interest rates and announced a stimulus package (quantitative easing). The market reacted negatively and the pound depreciated.
Bank of Japan (BOJ)
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) is also known as Nichigin. The bank’s Policy Board chairs annual policy meetings, decides on its approach to interest rates, and how it plans to influence inflation.
The Japanese government owns 55% of the bank, and 100% of its voting rights. The remaining 45% is publicly traded, traded as JASDAQ.
Since August 2019, the governor of the Bank of Japan is Haruhiko Kuroda, who has held the position since March 2013. He is currently serving his second five-year term, which will run until April 2023.

BOJ’s responsibilities
The main tasks of the Bank of Japan BOJ include:
- Maintaining the stability of the financial system: This job includes controlling currency and issuing paper money.
- Maintaining price stability: Exports are essential for Japan. Therefore, the Bank of Japan tries to keep prices as stable as possible.
To fulfill its responsibilities, the BOJ holds annual policy meetings (MPMs). MPMS are held eight times a year and last two days.
During that time the Policy Board (Governor, two Deputy Governors and six other members) will discuss and implement monetary policy. Since July 2018, the base rate has been set at -0.1% in the hope of economic growth.
The Bank of Japan’s Impact on the Yen
Japan has been experiencing a recession with very low inflation for the past few decades. They have consistently failed to achieve 2% inflation. The Bank of Japan has had to adopt a loose monetary policy, maintaining low interest rates in the hope of boosting the economy.
The USD/JPY exchange rate rose from 94.00 in March 2015 to 125.00 in June 2015 after Mr. Kuroda announced his first set of measures. And while it has fluctuated since then, the value of the yen was much lower when he became Governor. The USD/JPY exchange rate was around 108.00 in July 2019.
Swiss National Bank (SNB)
The Swiss National Bank (SNB) was founded in 1907. It is responsible for Swiss monetary policy and issues Swiss franc banknotes. As of 2015, the Swiss National Bank is privately owned, with most of the shares held by the Swiss cantons.
The main objective of the SNB
The main objectives of the Swiss National Bank SNB include:
- Price stability – Keeping exchange rates and/or inflation stable
- Economic Development – Focus on economic growth and stability
Note: However, the Swiss National Bank does not always raise interest rates when inflation is above target. In some cases, such as when GDP growth is low or negative, the Swiss National Bank may keep interest rates low to stimulate the economy.

Impact of SNB decisions
The Swiss National Bank (SNB) can influence the value of the Franc through expected change in interest rates. Traders should understand that currencies appreciate when expected interest rates rise, not just when nominal interest rates rise.
The foreign exchange market often prices current interest rate expectations. Changes in interest rates can cause the Franc to appreciate or depreciate.
Let’s take a look at the example below of EUR/CHF. In 2015 the Swiss National Bank surprised the market by removing the exchange rate cap on the Franc.
Swiss National Bank SNB lower interest rates when they are trying to boost the economy (GDP); raise interest rates when they are trying to curb inflation caused by an economy operating above potential (overheating).
Bank of Canada (BOC)
Canada’s central bank is called the Bank of Canada (BOC). Its mission is to ensure the stability of the Canadian economy and financial system. It does this through:
- Monetary policy implementation
- Financial system supervision
- Maintain the value and supply of Canada’s currency
- Public debt management
The central bank targets inflation between 1% and 3%, with a goal of keeping it stable around 2%. Since 1998, the bank has done a good job of keeping inflation within this range.
Monetary policy decisions at the BOC are made by consensus among the board of directors, which consists of the bank governor, senior deputy governor and four deputy governors. The executive council, which consists of the board of directors and the chief operating officer (COO), sets the bank’s strategic direction.
The Board of Directors of the Bank of Canada meets eight times a year.

Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA)
The functions of the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) are set out in the Reserve Bank Act 1959. Its mandate is to ensure a stable currency, full employment, and the economic prosperity and well-being of the Australian people.
The RBA Monetary Policy Committee consists of the central bank governor, deputy governor, secretary to the Treasury and six independent members. These individuals are appointed by the federal government.
The central bank targets annual inflation in the range of 2% to 3%. The committee meets 11 times a year, usually on the first Tuesday of each month, except January.

Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ)
New Zealand’s economy and monetary policy are overseen by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ), which is also responsible for maintaining sustainable levels of employment and a sound financial system.
The RBNZ has had an inflation target of between 1% and 3% since 2000. However, the bank is focused on its medium-term target of 1.5%, announced in late 2018. Failure to meet this target could result in the removal of the RBNZ governor.
Unlike other central banks, the final decision on monetary policy rests with the central bank governor. The bank’s committee meets eight times a year.

The impact of central bank vs forex
Forex traders closely monitor Central Bank interest rates. This is because they can have a significant impact on the Forex market. Institutions and investors tend to follow yields (interest rates). Therefore, changes in interest rates will lead traders to divert their investments to countries with higher interest rates.
Forex traders often evaluate the speech of the Central Bank Chairman. This gives them clues about whether the Central Bank is likely to raise/lower interest rates. The speech that explains the increase/lower interest rates is called Hawkish/Dovish.

Traders who believe the Central Bank is about to embark on a rate hike cycle will be bullish on the currency; while traders who anticipate a dovish stance from the Central Bank will be bearish on the currency.
The change in the benchmark interest rate provides trading opportunities based on the interest rate differential between two currencies of two countries through the “Carry Trade” strategy. Traders using this strategy seek to gain overnight interest by trading a high-yielding currency against a low-yielding currency.
How to trade when there are central bank interest rate decisions
Let’s look at a table summarizing possible scenarios when interest rate expectations change. Traders can use this information to make predictions about whether a currency is likely to increase or decrease in value.
| Market expectations | Reality | Impact on the foreign exchange market |
| Interest rates increase | Interest rates remain unchanged | Devalued currency |
| Interest rates fall | Interest rates remain unchanged | The currency appreciates |
| Interest rates remain unchanged | Interest rates increase | The currency appreciates |
| Interest rates remain unchanged | Interest rates fall | Devalued currency |
Conclusion
Understanding the impact of central bank vs forex means you have an important “compass” in your hand when investing in foreign exchange. Traders need to closely monitor every move from central banks, doing so will help you avoid unexpected risks and take advantage of profitable opportunities. This is a solid foundation for smart and effective forex trading. Wish you successful trading!
>>Read more:

