CFD capital management plays a critical role in helping traders protect their accounts, control risk, and achieve sustainable growth in highly leveraged CFD markets. As trading conditions become increasingly volatile and competitive, understanding how to allocate capital wisely is just as important as developing a strong trading strategy. This article will share the most effective CFD capital management principles and strategies, helping you not only to earn money but, more importantly, to keep it.
What is CFD capital management?
CFD capital management refers to the process of managing and allocating trading capital when trading Contracts for Difference (CFDs) in order to optimize profits while controlling risk. In a CFD trading environment that often involves high leverage, capital management is not just about dividing funds across trades – it also includes determining position size, risk per trade, and strategies to protect your account over the long term.
Many traders confuse capital management with risk management. In reality, capital management is a broader concept that includes overall financial allocation, while risk management focuses specifically on limiting losses in individual trades.

See more:
- What is CFD? Contracts for Difference Explained for Beginners
- Stock CFDs: What is it and How to Trade?
- What is CFD index investing and how does it work?
- CFD Forex: Why Do Investors Choose CFDs Instead of Direct Trading?
Why is CFD capital management crucial?
The CFD market is known for its high volatility and the ability to amplify both profits and losses through leverage. Without a clear capital management plan, traders can quickly lose their accounts after only a few consecutive losing trades. So, effective capital management helps traders:
- Protect accounts from unexpected market movements
- Maintain long-term trading sustainability
- Control emotions and avoid impulsive decisions
- Achieve consistent and sustainable profit growth

Core principles of CFD capital management
You don’t need complicated formulas to get started. Here are the fundamental principles that any investor must master:
Preserve capital before seeking profits
In CFD trading, capital preservation should always be the top priority. A trader may miss many opportunities, but losing the entire account eliminates any chance of future trading. A defensive mindset helps maintain long-term stability in the market.

Risk percentage per trade
One of the most widely used rules is risking only 1-2% of total capital per trade. For example:
- Account balance: $1,000
- Risk at 2% = $20 per trade
This approach helps minimize damage during losing streaks.
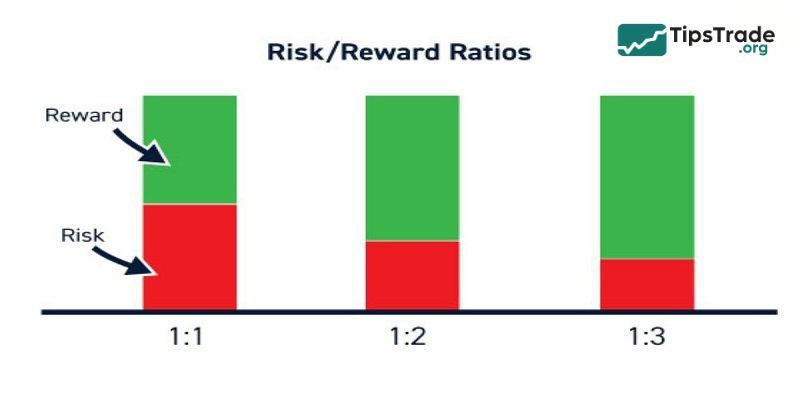
Risk/reward ratio in CFD capital management
The Risk/Reward (R:R) ratio measures the potential loss compared to expected profit. For example:
- R:R = 1:2 means risking $50 to potentially gain $100
Maintaining a healthy R:R allows traders to remain profitable even with a moderate win rate.
Position sizing management
Position sizing determines trade volume based on account size and acceptable risk. A basic formula is:
Position Size = Amount Risked / (Stop-Loss Distance × Pip Value)
A common mistake is choosing lot size emotionally rather than calculating it based on a structured plan.
Popular CFD capital management strategies
Fixed fractional position sizing
Fixed fractional position sizing is a method of allocating a fixed percentage of your total investment capital to each trade. It is a very popular and beginner-friendly approach. Instead of risking a fixed amount of money, you use a certain percentage of your account balance, typically ranging from 1-5%, depending on your risk tolerance.
Key principles:
- Define a fixed risk percentage for each trade (e.g., 0.2%–2% of total capital).
- Calculate the trade size based on this risk level and the distance between the entry point and the stop-loss level.
- Adjust position size as your account balance increases or decreases.

Advantages:
- Minimizes the risk of blowing your account since you never risk too much on a single trade.
- Flexible and suitable for accounts of all sizes.
- Easy to apply and does not require complex calculations.
- Long-term growth potential remains attractive thanks to the power of compounding.
Disadvantages:
- May limit profits if the account is small and the risk percentage is set too low. This depends on each individual’s risk tolerance as well as the trading strategy they use.
- Requires strict discipline to consistently follow the predefined risk percentage.
Pyramiding
Pyramiding is a trading strategy in which you progressively increase your position as the asset price moves in your expected direction. This method is particularly effective in bullish markets, helping maximize profits while minimizing risk if the trend reverses. The term “pyramiding” comes from the investment structure, where larger and safer positions form the base, while smaller and higher-risk positions are added toward the top.
Key principles:
- Start with an initial position, then add new positions as the price rises (in an uptrend) or falls (in a downtrend) once the trend is confirmed.
- Each new position is typically smaller than the previous one to control risk.
- Set stop-loss orders for each position to protect accumulated profits.
Advantages of Pyramiding
- Reduces premature exits: Pyramiding helps traders avoid closing positions too early when prices show minor signs of reversal. It encourages evaluating whether the change is a true reversal or just temporary, creating opportunities to add more trades.
- Compounding effect: By targeting assets with sustained upward trends, pyramiding promotes compounding returns while balancing potential profits and risks.
- Flexibility: Allows traders to adjust position sizes according to market movements, increasing or decreasing exposure when necessary.
Disadvantages of Pyramiding
- Requires a strong and sustained trend: Pyramiding is only effective if the asset price continues moving consistently in one direction over a period of time.
- Risk of significant losses: If the price reverses earlier than expected, the strategy can lead to substantial losses. Therefore, it is extremely important to strictly follow your stop-loss rules.
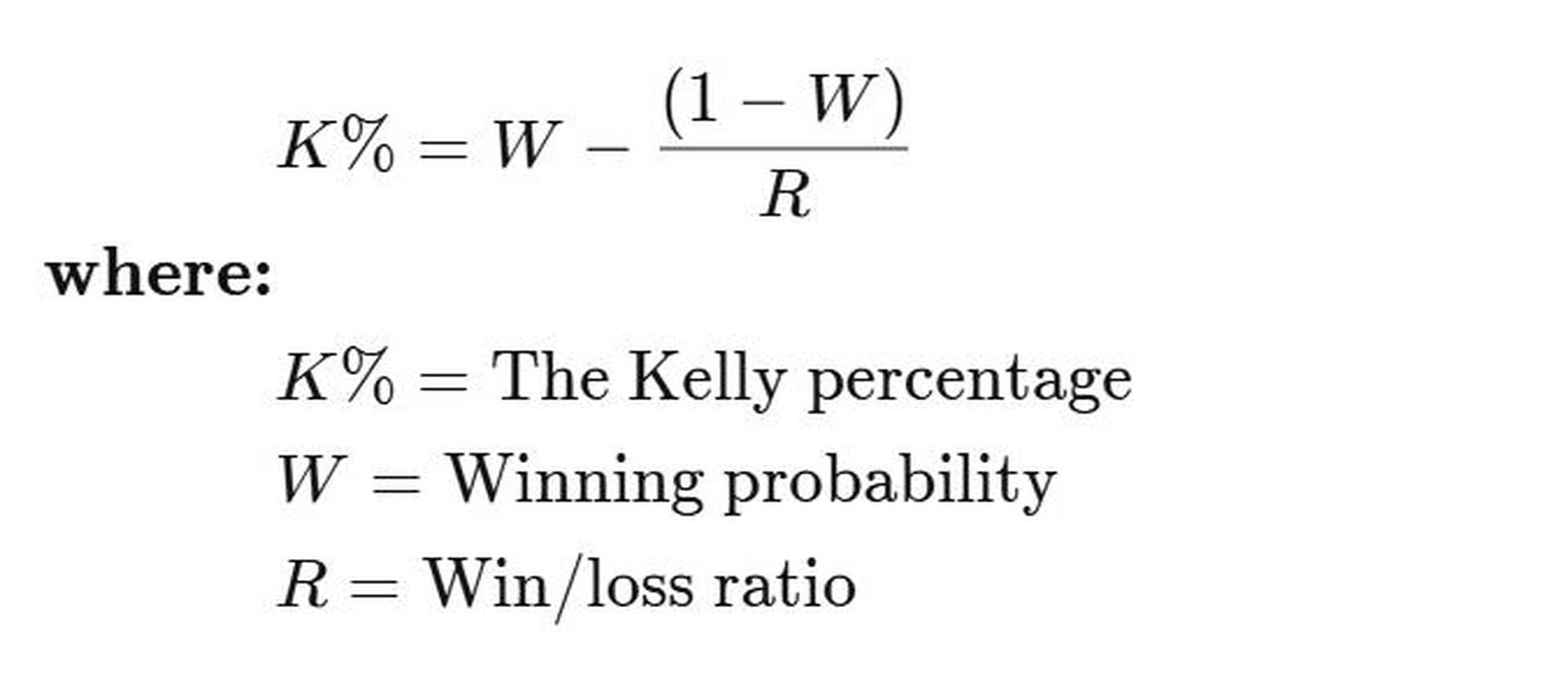
Kelly criterion
The Kelly criterion is a mathematical model used to determine the optimal percentage of capital to risk on each trade in order to maximize long-term returns while minimizing the risk of capital loss. The formula was developed by John L. Kelly Jr. and is particularly popular in trading and betting. It is considered a highly effective capital management model that many traders use in investing and trading.
In addition, this model allows you to simulate potential scenarios over many years, helping you fine-tune and optimize your capital management system in both investing and trading.
Kelly Formula:
Advantages:
- Optimizes long-term profits if you can accurately estimate your win rate and reward-to-risk ratio (R:R).
- Helps determine position size based on statistical data.
Disadvantages:
- Relatively complex, as it requires accurate data on winning and losing probabilities. Therefore, you need to continuously backtest your strategy to build a sufficiently large dataset.
- Difficult to implement because it requires mathematical knowledge and proficiency in Excel when creating simulations.
Mistakes to avoid in CFD capital management
- Overusing leverage: High leverage increases profit potential but also dramatically raises the risk of rapid account loss.
- Lack of portfolio diversification: Trading multiple CFD asset classes helps reduce concentration risk.
- Entering trades without a capital management plan: Each trade should have clearly defined risk, position size, and exit strategy.
- Increasing trade size after losses: This emotional reaction often leads to severe drawdowns and account failure.

Top tools for CFD capital management
Using Stop Loss and Take Profit
Stop Loss limits maximum loss, while Take Profit ensures profits are secured according to plan. Effective Stop Loss placement may be based on:
- Market structure
- ATR (Average True Range)
- Support and resistance levels
- Avoiding overly tight placements that can be easily triggered
Trading journals and performance tracking
- Keeping a trading journal allows traders to:
- Monitor win rates
- Analyze drawdowns
- Improve capital management strategies
CFD capital management calculators
- Position size calculators
- Risk calculators
- Trading analytics tools such as Myfxbook or Edgewonk
Final thoughts
CFD capital management is a critical factor for both traders and investors participating in CFD trading. No matter how effective your trading strategy is, without strict capital management, the risk of blowing your account is always present. The three methods presented in the article above offer different approaches, suitable for various levels of experience, profit goals, and risk tolerance. Start developing your CFD capital management skills today to become a smarter and more disciplined investor.
See more:

