What is Stop Loss? Stop Loss (SL), or the cut-loss order, is an essential tool in trading that helps traders protect their capital and manage risk effectively. In volatile markets like forex, Stop Loss can be a “shield” that prevents significant losses while helping you maintain trading discipline. This article will explain in detail what Stop Loss is, why it is important, effective ways to set SL, and the mistakes to avoid. Let’s explore to enhance your trading skills!
What is stop loss?
What is stop loss? Stop Loss (abbreviated as SL) is an automatic order placed in the trading platform that helps close a trade when the price reaches a predetermined level to limit losses. In other words, Stop Loss acts as a “shield” protecting traders’ accounts from unfavorable market fluctuations.
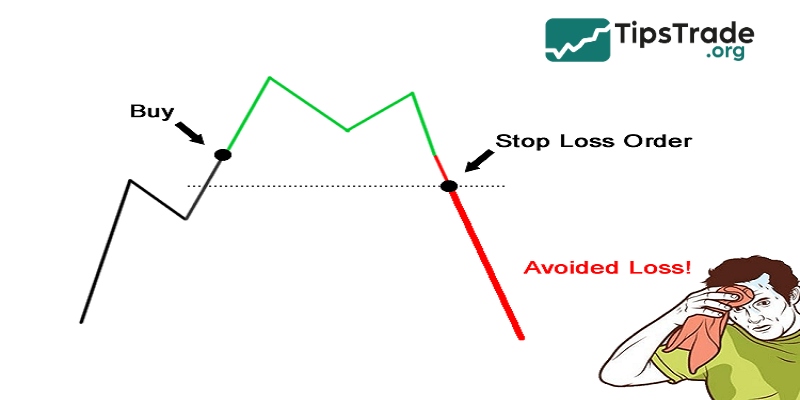
>>Read more:
- What is Forex? The Complete Guide for Beginners
- What is Drawdown Forex? How to determine it? What is a good Drawdown ratio?
- Essential Forex Orders every trader must know
- What is Forex Technical Analysis and How Important is it?
How stop loss orders work
For a Buy order, the stop loss is a price level below the entry position (< execution price). If the market moves against expectations, the price drops and hits the stop loss, your order will be automatically closed. At the same time, the trading software will automatically deduct the loss from your balance (account balance).
Conversely, for a Sell order, the stop loss is a price level above the entry point (> the execution price). If the market moves against your prediction, meaning it rises and hits the stop loss, your order will be automatically closed. The loss will be deducted from the balance when the order is closed, just like in the case of a Buy order.
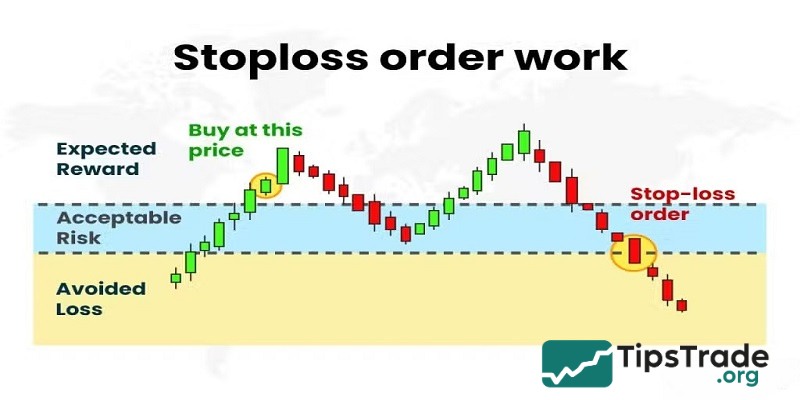
The importance of using stop loss orders in forex
Stop loss orders play an extremely important role for traders when trading forex. Details are as follows:
- Effectively limit risk: Set a stop-loss order to ensure you only incur a fixed loss even if the market fluctuates unexpectedly. This is a tool to protect your account from sudden price shocks.
- Protect your account against unforeseen mistakes: Even with a good trading strategy, you can still mispredict the market. Setting a stop-loss order will help you avoid losing all your capital just because of a few wrong trades.
- Reduce the impact of emotions in trading: Once you have set a stop loss, you do not need to hold the position in the hope that the market will turn around. This helps you trade more rationally, avoiding being swept away by negative emotions.
- Create conditions for disciplined trading: SL is an important tool in forex capital management. When you always adhere to the predetermined SL level, you can calculate the risk for each order in advance and allocate the trading volume appropriately.
>>Read more:
- What is forex trading? A detailed guide to forex trading from A – Z
- Top 10 best forex currency pairs to trade in 2025
- Forex Trading Hours – The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide
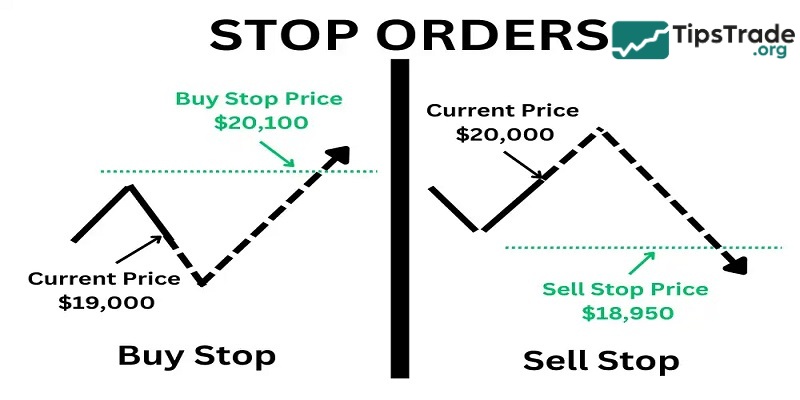
Types of stop loss orders
You can use various types of stop-loss orders, depending on your investment strategy. Some orders provide a simple mechanism for triggering a sale, while others offer more flexibility in execution. Below are three common types that you may consider:
Standard stop loss order
This is a basic stop-loss order, which will be converted into a market order when the price reaches the specified level. This ensures that the order will be executed, but does not guarantee a specific selling price.
For example, if an investor buys a stock at $75 and sets a stop-loss order at $70, the stock will be sold when the price hits this threshold, although the final execution price may be lower.
Trailing stop loss order
This is a type of stop-loss order that is flexibly adjusted based on price movements, which is beneficial for investors. Instead of setting a fixed stop price, the stop price will move with the stock at a certain percentage or dollar amount.
For example, with a 5% trailing stop-loss order for a stock purchased at 00, the initial stop price would be set at $95. If the stock rises to 10, the stop price will increase to 04.50, which is 5% lower than 10. If the price then falls, the stop order will be triggered at 04.50.

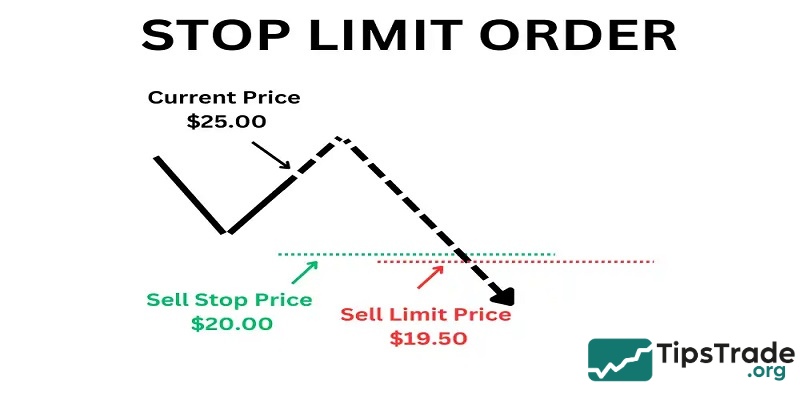
Stop limit order
In reality, a limit stop order isn’t exactly a type of stop-loss order, but it functions quite similarly and can also be used for risk management. The difference is that instead of becoming a market order, it will become a limit order at the specified price. This helps avoid selling at a price lower than the limit investors desire. However, unlike a stop-loss order, a stop-limit order carries the risk of not being executed if the price moves too quickly.
For example, if an investor buys a stock at $40 and sets a stop price at $35 with a limit of $34, the stock will only be sold at $34 or higher, and the order may not be executed if the price drops too quickly.
Methods of placing stop loss orders
Effectively setting a Stop Loss requires a combination of market analysis and capital management. Below are three common methods for establishing SL:
Based on technical analysis
Technical analysis can help you identify important price levels to set stop-loss orders. This protects you from unfavorable price fluctuations while still allowing trades to have room to develop.
- Strong support and resistance levels: You can place stop loss below the nearest support level in a buy trade or above the nearest resistance level in a sell trade.
- Moving Averages (MA): Set stop loss belowMA line important levels (e.g. MA 20, MA 50, MA 200) can help you exit a trade when the trend shows signs of reversing.
- Trendlines: If you are trading with the trend, you can place your stop loss below the uptrend line (for buy orders) or above the downtrend line (for sell orders).
- Chart Patterns: Price models like triangle, rectangle, head and shoulders,… can suggest potential stop loss levels based on the structure of the pattern.
- Volatility Indicators: Indicators like ATR (Average True Range) can help you measure market volatility and set your stop loss accordingly. Stop losses should be wider when the market is volatile and narrower when the market is less volatile.
- Fibonacci Retracement Levels: The levels FibonacciRetracements can act as potential support and resistance levels, helping you determine where to place your stop loss.
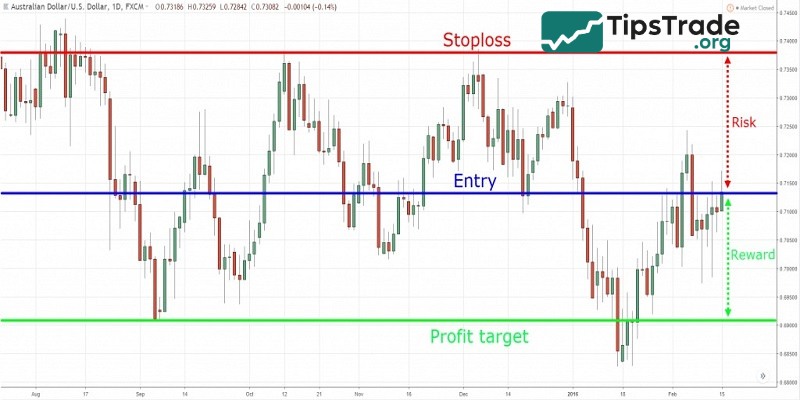
Based on the risk/reward ratio
Determine the desired risk/reward ratio, for example 1:2 or 1:3, meaning you accept a risk of 1 unit to earn 2 or 3 units of profit. The stop loss (SL) is set to ensure that the potential profit ratio is higher than the risk.
For example: You buy the USD/JPY pair at 150.00, with a profit target of 151.50 (150 pips). With a 1:3 ratio, set the SL at 149.50 (50 pips), ensuring that the risk is only 1/3 of the expected profit.
Based on trading volume and capital management
This method calculates Stop Loss based on the amount of capital you are willing to risk (usually 1-2% of total capital) and the trading volume. The distance from the entry point to the SL is determined to ensure that the loss does not exceed the defined risk level. This will help you protect your account from consecutive losing streaks.
Common mistakes when using stop loss
Despite being a powerful tool, many traders still make mistakes when using SL. Here are some common mistakes and how to fix them:
- Set Stop Loss too close: This can cause your order to be triggered by small market movements, and then the price moves in the direction you predicted. Remember that there is always some noise in the market.
- Set Stop Loss too far away: On the other hand, placing a Stop Loss too far away will not protect your account effectively. If the market moves against the trend you predicted, you may incur larger losses than necessary.
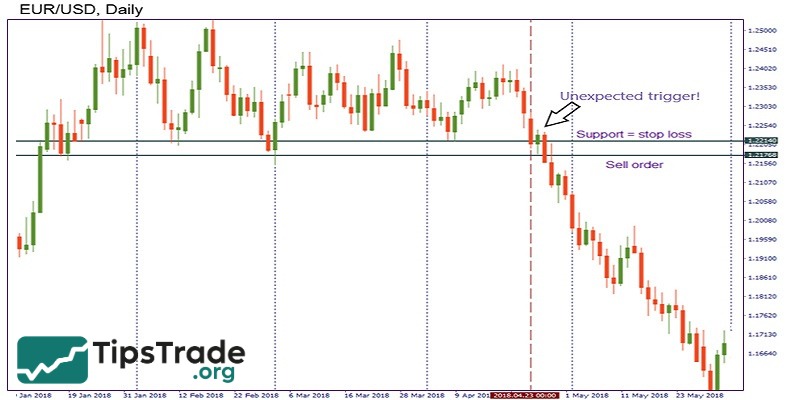
- Place Stop Loss at important support and resistance levels: These are areas where many other traders also place Stop Loss orders. This can cause the “whales” to take advantage of “sweeping” your Stop Loss before the price follows the main trend.
- Use a fixed Stop Loss level for every trade: Each trade and each currency pair/asset has different levels of volatility. Applying a fixed Stop Loss level may not be appropriate and result in the order being triggered too early or too late.
- Do not adjust Stop Loss when the market moves in your favor: When your trade is profitable, adjusting your Stop Loss in a favorable direction (e.g. moving your Stop Loss to breakeven or profitable) can help you lock in profits. Many traders skip this step.
- Set Stop Loss based on emotions or specific amount willing to risk: Stop Loss placement should be based on technical analysis and market structure, not just on fear of loss or a specific dollar amount.
- Do not use Stop Loss: This is the most serious mistake. Not setting a Stop Loss means you are taking unlimited risk on your trade.
FAQ about what is stop loss
Is Stop Loss suitable for beginners?
Yes. Stop Loss is particularly suitable for beginners because it helps protect the account from significant losses. New traders are often easily swayed by emotions, so setting a Stop Loss creates a “safety barrier,” helping them maintain trading discipline.
What is the difference between Stop Loss and Stop Limit?
- Stop Loss Order: When the price reaches the set level, the order will automatically convert to a market order (selling immediately at the market price). The advantage is that it ensures the position is exited, but the execution price may differ from the predetermined level.
- Stop Limit Order: When the price reaches the trigger level, the order will only be executed if the market price is within the chosen limit. The disadvantage is that it may not be executed if the price moves too quickly.
Can I trade without Stop Loss?
In theory, you can trade without a Stop Loss. However, this is an extremely risky strategy, as just one sudden strong fluctuation can “wipe out” your account. Even professional traders often use Stop Loss to protect their capital.
How much percentage should I set for Stop Loss?
A common rule is to risk 1-2% of your account capital for each trade. For example, if you have 10,000 USD, the maximum risk should be limited to 100-200 USD per trade. This helps minimize the risk of account depletion when a losing streak occurs.
Final words
SL (Stop Loss) is not just a simple trading tool but also a golden principle, unchanging in risk management. Understanding the concept of “What is Stop Loss” in trading and knowing how to use it effectively is a key factor in protecting capital, maintaining discipline, and increasing the chances of success in the challenging financial market. Consider Stop Loss as a reliable companion on your trading journey.

