Forex spread explained is a basic concept, yet it often confuses new traders. Understanding how to calculate spreads in forex and the phenomenon of spread widening will help you control costs and avoid risks. This article will provide you with a clear and simple explanation of what spread in forex is, along with the essential knowledge you need.
Forex spread explained
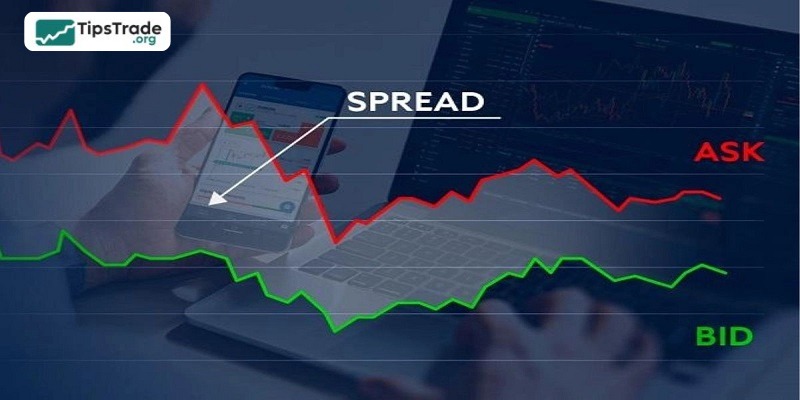
In the world of foreign exchange trading, forex spread explained is a fundamental yet extremely important concept that every trader needs to understand. Simply put, the spread is the difference between the buying price (Bid) and the selling price (Ask) of a currency pair.
Imagine going to a bank to exchange money. The bank will quote two prices: the buying price (Bid) – the price at which they are willing to buy foreign currency from you, and the selling price (Ask) – the price at which they sell foreign currency to you. The spread is the difference between these two prices.
Example: The USD/VND exchange rate is quoted at 24,580 / 24,860.
- 24,580 is the Bid price (the bank buys USD from you).
- 24,860 is the Ask price (the bank sells USD to you).
- Spread = 24,860 − 24,580 = 280 VND.
The spread is not only a trading cost that you have to pay, but also the primary source of income for brokers. Most online trading platforms today apply floating spreads, meaning the spread changes in real time to reflect market volatility.
- Guide to using TradingView chart for beginners
- NFP Forex Strategy: A Complete Guide for Every Trader
- How to read and use the economic calendar for forex in trading
- The 5 Best Forex Volatility Indicators Every Technical Trader Should Know
How to calculate the spread in forex
In forex trading, spread is a fundamental concept that you need to clearly understand. The spread is the difference between the buying price and the selling price of a currency pair.
Formula: Spread = Ask – Bid
Where:
- Selling price (Ask): The price at which you buy.
- Buying price (Bid): The price at which you sell.
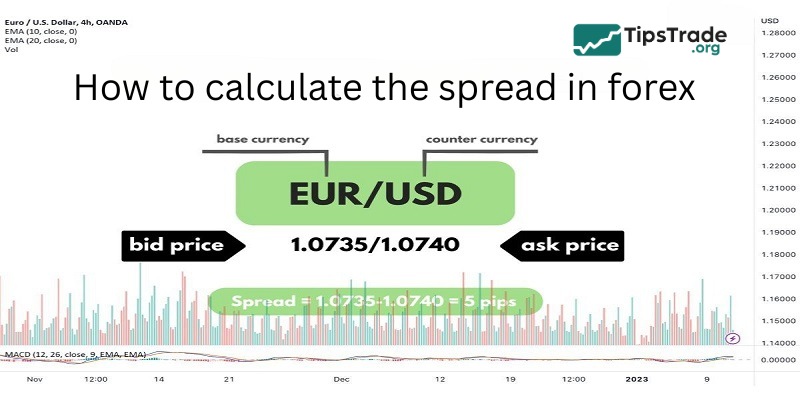
Example: The EUR/USD pair is quoted at 1.1050 / 1.1052.
- Buying price (Bid): 1.1050
- Selling price (Ask): 1.1052
- Spread = 1.1052 − 1.1050 = 0.0002
Understanding how to calculate Forex spread explained not only helps traders accurately estimate trading costs but also plays a key role in managing investment strategies effectively. This is because the spread can significantly impact the profit or loss of each trade, especially when applying short-term strategies or trading with large volumes.
Two main types of spreads in Forex trading
Fixed spread
A fixed spread in forex is similar to a quoted price that remains unchanged regardless of market fluctuations. The advantage of this type of spread is its stability and predictability, which helps traders better control their trading costs. However, fixed spreads are usually higher than floating spreads because brokers need to ensure profits under all market conditions. Therefore, when trading during calm market periods, a fixed spread may result in higher costs.
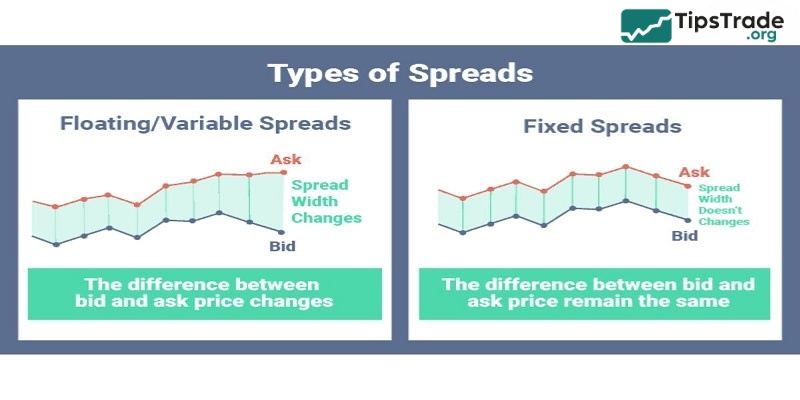
Floating spread
A floating spread in forex is like ocean waves, sometimes calm, sometimes turbulent, constantly changing in line with market movements. The main advantage of this type of spread is its flexibility, often offering lower costs than fixed spreads, especially when the market is stable. As a result, traders can reduce transaction costs and better seize market opportunities. However, just like the sea, floating spreads also carry unpredictable risks.
When the market becomes volatile due to economic events or strong price fluctuations, spreads can suddenly widen, causing trading costs to surge and potentially “eat into” or even wipe out your profits.
Factors affecting Forex spread
Spread in Forex is not a fixed constant but continuously fluctuates, influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors will help you predict spread fluctuations, thereby controlling trading costs and making effective investment decisions. Below are some key factors:
Currency volatility
When a country’s monetary policy is poorly managed or highly unstable, its national currency tends to experience strong fluctuations. To compensate for the increased risk, the selling price is often pushed higher, resulting in a wider spread.
Liquidity of financial assets
Liquidity refers to how easily an asset can be bought or sold. This factor has a direct impact on the spread in the market.
- Currency pairs with high trading volume such as EUR/USD and USD/JPY usually have narrow spreads due to high liquidity and continuous trading.
- Less popular currency pairs or exotic pairs tend to have wider spreads because of lower liquidity and fewer market participants.

Economic and social risks
Political and economic instability in a country can significantly affect exchange rates. Factors such as political crises, sudden changes in government, or poor economic management often lead to rapid currency depreciation, accompanied by high inflation. In such situations, sharp currency fluctuations increase risk and reduce liquidity, causing spreads to widen.
Trading volume
In large-volume transactions that can cause strong market price movements, market makers may adjust spreads to compensate for the risks they bear. However, in reality, the forex market has extremely high liquidity, so small retail traders are unlikely to have any significant impact on market prices.
What is spread widening in Forex?
In forex trading, the spread (the difference between the buying price and the selling price) usually fluctuates within a certain range. However, at times the spread can suddenly “widen”. This is known as spread widening. It is similar to going to a bank to exchange money and suddenly noticing that the gap between the buying and selling prices has increased significantly.

Causes of spread widening
Spread widening often occurs when the market is “quiet,” with fewer participants trading a particular currency pair. This usually happens during weekends, early morning hours, or with less frequently traded currency pairs. When liquidity is low, the number of market makers also decreases, leading to less competition and higher spreads.
The forex market is constantly changing, and strong price movements are one of the main causes of spread widening. When important news, unexpected political events, or other sources of uncertainty occur, market makers adjust spreads to compensate for the increased risk. In this case, spread widening acts like a defensive reaction of the market to volatility “storms.”
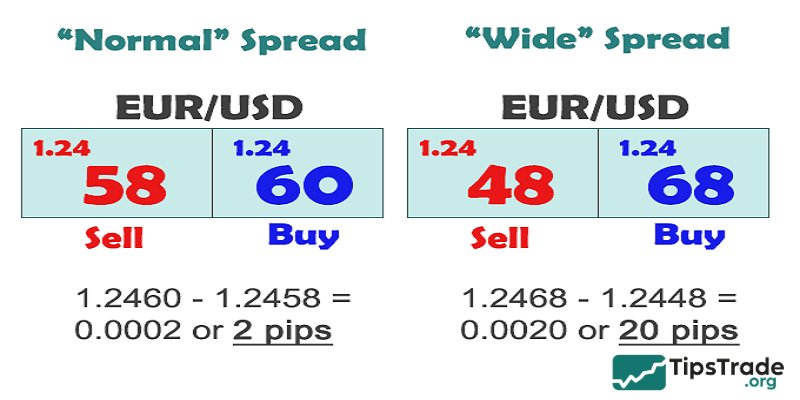
Although it is not the primary factor, some brokers may also influence spreads. During certain periods, they may deliberately widen spreads to increase profits. Therefore, choosing a reputable broker that is transparent about spreads is essential to ensure you are not unfairly “overcharged.”
Notes when facing spread widening
- Spread widening means that your trading costs increase. This can significantly impact your profits, especially for short-term trades.
- When spreads widen, your orders may be harder to execute or may be filled at unfavorable prices (slippage).
- Spread widening is often accompanied by strong market volatility, which increases the risk of losses. Particularly when you are using high leverage.
Conclusion
Forex spread explained and how to calculate it simply have just been detailed by Tipstrade.org in the content above. Understanding how to apply spreads effectively will help you optimize profits and limit risks. We hope that this content provides you with additional useful knowledge.

